In a recent piece for The New York Times, Maud Newton makes the suggestion that David Foster Wallace’s essays — more than Cheetos, beer, amusing cat videos, and Jolt Cola — are largely to blame for chatty Internet discourse. Newton suggests that Wallace’s “Tense Perfect” (a review of Bryan Garner’s Dictionary of Modern American Usage collected in Consider the Lobster as “Authority and American Usage”) is “as manipulative in its recursive self-second-guessing as any more straightforward effort to persuade.” She tries pinning the mimetic transmission of Wallace’s syntax on “Dave Eggers’s literary magazine and publishing empire,” but doesn’t offer a single example (save for Eggers’s “Rules and Suggestions for Enjoyment of This Book,” a citation so overbroad that it can equally apply to the notice about shooting anyone in search of a plot at the head of The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn). Newton cites David Foster Wallace’s “E Unibus Pluram” as the “ur-text of this movement,” but fails to establish much beyond cannibalizing a thoughtful Keith Gessen essay from eleven years ago (as well as its AO Scott antecedent). She then concludes that “the idea of writing is to provoke and persuade, not to soothe. And the best way to make an argument is to make it, honestly, passionately, without regard to whether people will like you afterward.”
It’s too bad that Newton lacks the logos and the level head to heed her own advice, and that she can’t level with us about her bilious biases. Conflation is not persuasion, nor is cleaving to one’s syntactic prejudices a reliable way of responding to an argument. Newton’s essay comes off as the work of a careless and needlessly furious blogger who has been given an unanticipated platform, not someone who takes the art of writing (and thinking about writing) seriously. There are numerous problems with her argument, as sloppy and as derivative in its thinking as the self-congratulatory folderol Newton claims to have abandoned during an apparent halcyon intellectual period sometime after the age of 20, where she “was forced to confront serious practical and ethical questions” in law school. (Those ethics took Newton a long way in 2008, when Newton was offered a paid junket trip to England by a publisher, and, by her own admission, accepted the quid pro quo “within a half-hour of receiving the offer.”)
Like any common and overworked lawyer massaging boilerplate from practice guides, much of Newton’s “argument” about Wallace’s regular guy schtick has been cribbed from this 2002 Languagehat post. Newton complains of the “I’m-just-a-supersincere-regular-guy-who-happens-to-have-written-a-book-on-infinity approach.” Languagehat’s Stephen Dodson complains that “[t]his sort of smarmy regular-guy rhetoric from someone who knows you know he’s a famous author and who is setting himself up as an all-knowing authority makes me sick.” Dodson, however, had the decency to be transparent about his fury, confining his gripes to the article in question. What’s especially striking is that Newton, cognizant that she is writing for The New York Times, adopts the self-same “regular gal schtick” for her piece. And it is with this simplistic stance that Newton reveals her reductionist stature as a thinker.
Instead of using specific examples to provide a helpful lexical lineage for her claims (citing, for example, the very blogs impaired with Wallace-inspired banter), Newton offers little more than unfounded and dimly ironic speculation that has nothing to do with Wallace:
I suppose it made sense, when blogging was new, that there was some confusion about voice. Was a blog more like writing or more like speech? Soon it became a contrived and shambling hybrid of the two. The “sort ofs” and “reallys” and “ums” and “you knows” that we use in conversation were codified as the central connectors in the blogger lexicon. We weren’t just mad, we were sort of enraged; no one was merely confused, but kind of totally mystified. That music blog we liked was really pretty much the only one that, um, you know, got it. Never before had “folks” been used so relentlessly and enthusiastically as a term of general address outside church suppers, chain restaurants and family reunions. It’s fascinating and dreadful in hindsight to realize how quickly these conventions took hold and how widely they spread. And! They have sort of mutated since to liberal and often sarcastic use of question marks? And exclamation points! “Oh, hi,” people say at the start of sentences on blogs, Twitter and Tumblr these days, both acknowledging and jokily feigning surprise at the presence of the readers who have turned up there.
Let’s do the work that Newton couldn’t be bothered to do. Because if you’re going to promulgate information about the methods and manner in which people use language, then it’s important to consider the whole larder.
One can spend a lifetime ruminating upon “uh” and “um,” which psychologists have recently suggested play roles as conversational managers. But what Newton is trying to peg here is speech disfluency — specifically, those fillers often emerging as one is deliberating over a thought. Fillers hardly originate with Wallace, nor are they confined to English. To offer one historical example, here’s some glorious dialogue from The City Wives’ Confederacy — a 1705 play written by Sir John Vanbrugh:
Cor. Let me read it, let me read it, let me read it, let me read it, I say. Um, um, um, — Cupid’s — um, um, um, — Darts, um, um, um, — Beauty, — um, — Charms, — um, um, um, — Angel, — um, — Goddess, — um, [Kissing the letter.] um, um, um, — truest Lover, — um, um — eternal Constancy, — um, um, um, — Cruel, — um, um, um, — Racks, — um, um, um — Tortures, — um, um, — fifty Daggers, — um, um, um, — bleeding Heart, — um, um, — dead Man, — Very well, a mighty civil letter, I promise you; not one smutty word in it: I’ll go lock it up in my comb-box.
For full effect, try reading that passage aloud. What sounds seemingly annoying in textual form becomes positively poetic as you’re saying it. But Vanbrugh didn’t stop there. We find this exchange in Scene II:
Mon. Um — a guinea, you know, Flippanta, is —
Flip. A thousand times genteeler; you are certainly in the right on’t; it shall be as you say — two hundred and thirty guineas.
Mon. Ho — Well, if it must be guineas — Let’s see — two hundred guineas —
Flip. And thirty; two hundred and thirty.
Now imagine that some snotty journalist or critic had told Vanbrugh that he couldn’t use “um” or “you know” or “let’s see” in his dialogue because, if he had published these words, they might be codified as the central connectors in the theatrical lexicon. If Vanbrugh’s dialogue had been scrubbed, how then might we have known — in a time before movies, gramophones, and computers — how people talked? One can hardly imagine reading masterpieces like The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn or Finnegans Wake in anything other than their unique patois. Therefore, should one be so needlessly tendentious when it comes to blogs?
Newton’s feckless fig isn’t really about what Wallace (or any blogger) has to say. It’s about how they say it. As anyone who has waded through academic papers knows, there are often brilliant kernels contained inside dense and impenetrable style. But a person of true and eclectic intellectual rigor wouldn’t hold the thinker accountable based solely on the syntax.
Since Newton is unable to establish a clear connection between Wallace and “the stylized mess that is Gen-X-and-Y Internet syntax” (and unable to comprehend that many of these syntactical eccentricities have recirculated for centuries), we are therefore forced to conclude that Newton is needlessly hostile to any sentence that isn’t written in the plain and vanilla language that she holds so dear to her cold and humorless heart.
This is the position of a lexical reactionary, not just a Wallace hater. Because if Newton were genuinely interested in language or people or the often magical way that words are transmitted in our culture, she wouldn’t be so quick to condemn. She would actually do the legwork and use these findings to offer a persuasive argument instead of outsourcing it to her readership (“Visit some blogs…to see these tendencies writ large,” “The devices can be traced back to him, though…,”). Is that not persuasion? But Newton isn’t interested in listening to anything other than the sound of her own voice — the vitiated “plain question and plain answer” ideal plucked from Life on the Mississippi that, in Newton’s uncomprehending hands, becomes more inimical than imitable. She doesn’t understand that distinct writing can often be forged from imitation — as the many fresh talents who have mimicked Hemingway (Ann Beattie, Raymond Carver, Hunter S. Thompson) can attest. And in telling New York Times readers that imitation and repetition are wrong or “dreadful in hindsight,” Newton reveals herself to be committed to the act of expressive conformity. The Newtonian ideal, rooted in misanthropic nihilism, leaves no room for prototypes or apprenticeship — even though, having shed the burden of “her own archives,” she cannot actually lodge a proper argument here. In short, Maud Newton has transformed into a cultural atavist who argues along the lines of Lee Siegel. You can respond to her argument, but only using the words and the terms that she has established. (And as Joe Winkler has argued, why should Wallace be judged by foreign standards?)
When contemplating the state of culture and language, it helps to view the reuse of expressive terminology through context. A helpful linguistic anthropology volume authored by Alessandro Duranti suggests that “Oh, hi!” has been in use — largely over the telephone or after an awkward social encounter — decades before Wallace published a single word. “Oh, hi!” is modeled on “Ah ciao!” “Oh” initially appeared before “hi” when the answerer awkwardly attempted to return a greeting without knowing the greeter’s name. So it makes sense that someone using Twitter or Tumblr, unaware of the sheer scale of readers, would start a post this way. (And to return to Gessen’s essay, this might very well reflect his humorous aside that “in the long run books are not written for the editors of prestigious magazines or the professors of fashionable theories.” In other words, speculating on a readership is best left to the crass and artless marketers.)
Newton is right to suggest that the intersection between writing and speech is what led to the early conversational feel of blogs, but she never considers the possibility that those who were sending their thoughts and feelings into the electronic ether truly had no idea who they were reaching. (On the “Oh, hi” question, she does concede midway through the piece that those who write this way may be simultaneously “acknowledging and jokily feigning surprise.” But observe the strange suspicion here. Sometimes a cigar is just a cigar. It’s telling that Newton’s article offers no space for sincerity, that the Newtonian ideal involves directness without nuance or irony.) She assumes that most of the early bloggers were readers of Wallace and Eggers, rather than those who may very well have left the house and conversed with fun and interesting people. It doesn’t occur to Newton that, in using words like “folks,” bloggers were using the very voices they might employ in everyday conversation. And just as we’ve seen in the Vanbrugh play, the Internet’s early days (at least, what we’ve been able to preserve of them) offer us an unprecedented treasure trove of how certain phrases and words made their way into our vernacular. Much as digital cameras have ushered in an age that is the most photographed in human history, digital conversation has afforded us an equally vast and limitless tapestry.
So Newton’s blinkered prohibition of “folks” outside of some implied Midwestern setting is not only needlessly condescending, but it suggests that writing in one’s voice is rooted almost exclusively in mimicking trendy magazine articles rather than responding to conversational cadences. This isn’t a question of being liked or craving admiration and appeal. It’s about speaking in terms that keep the conversation, whether contentious or conciliatory, alive.
Internet culture was built in large part by smart people being trapped in soul-sucking jobs and desiring to connect with others. In “E Unibus Pluram,” Wallace identified television as “an absolute godsend for a human subspecies that loves to watch people but hates to be watched itself.” The time has certainly come to unpack some of these arguments into something that includes the Internet’s complexities. But Newton isn’t sharp enough to build from Wallace’s points, even as she disagrees with him. She cannot, for example, consider the obvious truth that, in an era of Twitter and Google Plus, the watchers have become the watched. Rather than serving up a plainspoken exemplar within her essay that articulates an original point and lives up to her declared ideal (or puts her on the line, as Zadie Smith did in her Facebook essay when confessing “not being liked is as bad as it gets”), the great irony here is that Newton herself has soothed her readership using the very methods that Wallace (and Newton in failed ironic mode) condemned. Newton, by publishing her essay at The New York Times instead of her blog, craves the very admiration and approval she dismisses as toxic. She wants to be read, but she is not especially interested in practicing the very intellectual rigor she champions. Because if she were, she would be crystal-clear in establishing her terms. She cannot identify even one of the many critics “making their arguments in this inherently self-undermining voice.” Who are these mysterious Wallacites wandering in the woods? Do they have axes and are they killing bitter attorneys who can’t finish their novels (and have an infuriating need to report constantly on this)? Does Newton really think so little of Wallace readers or bloggers that she cannot consider the possibility that they may very well be influenced by other authors? She thus undermines her own argument.
Newton’s spectacular failure to consider these subtleties may have something to do with not steeping herself in Wallace’s complete catalog. The phrases “plus, worse,” “pleonasm,” and “What this article hereby terms a ‘Democratic Spirit'” come from the very essay (“Tense Perfect”) she commends as “one of his best and most charming essays,” yet not from the same paragraph. “Totally hosed” comes from the famous 2005 Kenyon commencement. In other words, the only four Wallace texts that Newton has consulted for her piece are three essays: “E Unibus Pluram” (1993), “Authority and American Usage” (1999), “Big Red Son” (1998), and the Kenyon address. It seems to me that if you’re going to do a David Foster Wallace takedown, you should rely on a good deal more than the usual greatest hits. That’s a bit like writing about the Beach Boys when you’ve only heard “Good Vibrations” once.
Newton’s piece is less about offering a new argument or repudiating an old one, and more about expressing an uninformed position on Wallace and linguistics. It’s about standing against the possibilities of language and ideas. It’s about dictating the terms of how one should think while disingenuously suggesting that the reader can think for herself.
That’s a skill set that comes quite naturally to an embittered tax attorney. But it’s somewhat amazing that such a misleading and superficial approach would be welcomed by the ostensible Paper of Record.
UPDATE: Some additional responses:
(1) The New Inquiry‘s Matt Pearce, who notes that “Newton’s criticism obscures the fact that she and Wallace have more in common on intellectual honesty and integrity and straightforwardness than her essay lets on.”
(2) Callie Miller, who writes, “Life is short, wars are being fought, loved ones are dying every day…must we really be so intense about our books?” That’s a very good question.
(3) Alexander Chee, who agrees more with Maud Newton than I do, writes that Wallace “was a writer whose work gave back a vision of the world that pierced the scrim of the fear we were all feeling. If we imitated him, or imitated each other imitating him, really, I think we did it because of how we all wanted to find our way through. But it became like a game of telephone, but with style, and what had once been able to clarify something soon obscured them.”
(4) Glenn Kenny, who worked at Premiere when “Big Red Son” came in, clarifies what Wallace meant by the “sort of almost actually” fillers that Newton bemoans: “Each one, as we see, serves a different function, or I should say, implies a different state of mind, and each state is competing with the other. By the point in the essay at which the description of Goldstein arrives, the reader ought to have sussed out that Wallace has some very substantial problems with both pornography and the industry that produces it. But he’s also been bracingly honest about the attraction that walks hand in hand with his repulsion, and when he’s not going at his subject with something resembling all-out disgust (as in the passages about Paul Little, a.k.a. Max Hardcore), there’s a bracing and troubled honesty at work here, as in all of Wallace’s essayistic work, a desire to get at moral truth without being, well, moralistic; and a constant ambivalence.”
(5) CulturePulp’s Mike Wallace writes: “But for Maud Newton to also join a parade of lesser writers staking out lit-cred for themselves by throwing the freshly dead Wallace under the bus — and then to passive-aggressively blame him for all sorts of not-his-fault jackassery — is for me to sort of politely tell Maud Newton to piss off.”
(6) Matt Kiebus: “If Ms. Newton wants to live in a world where people make arguments ‘straightforwardly, honestly, passionately and without regard to whether people will like you afterward,’ that’s her choice. And although I think she may need a fucking time machine to find the world she’s looking for, I still respect her opinion.”
(7) The Oncoming Hope: “Newton seems to conflate unserious language with Southern dialectical norms, which is all the more surprising given how many times she’s blogged about the liveliness of Southern Texan vernacular.”
(8) Weeks later, the Huffington Post‘s Omer Rosen begins a multi-part offering (with Casey Michael Henry) on David Foster Wallace’s appropriation.

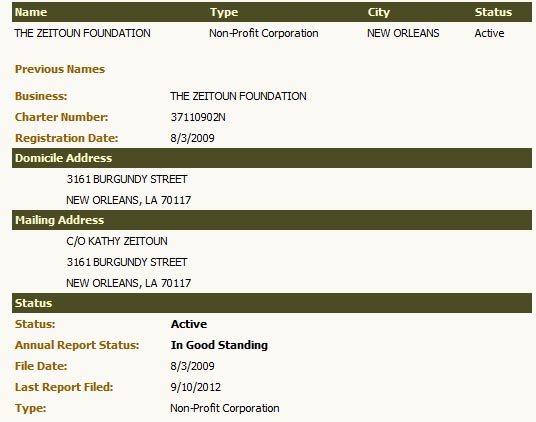

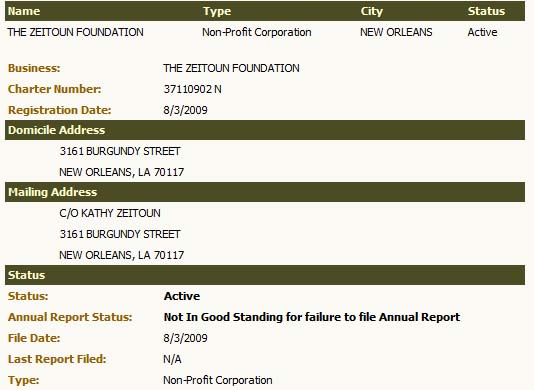

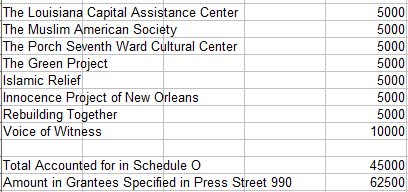
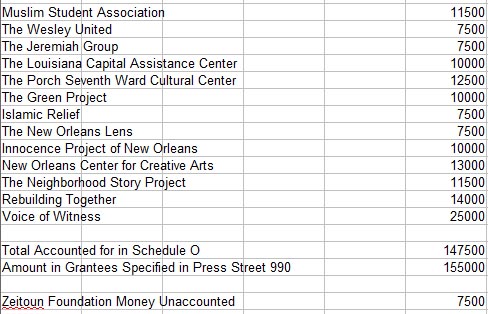


 The SF Weekly‘s Joe Eskenazi
The SF Weekly‘s Joe Eskenazi 
 If prosperity remained just around the corner, one could at least take comfort with the handsome issue, which came, as promised, with contributions from Stephen King, Nicholson Baker, and William T. Vollmann. But the more important question of whether the San Francisco Panorama was profitable was swept under the rug. Then last month, The Awl‘s Choire Sicha
If prosperity remained just around the corner, one could at least take comfort with the handsome issue, which came, as promised, with contributions from Stephen King, Nicholson Baker, and William T. Vollmann. But the more important question of whether the San Francisco Panorama was profitable was swept under the rug. Then last month, The Awl‘s Choire Sicha