On April 24, 2011, the Scottish edition of The Sunday Times published “Rankin admits Twitter addiction” on page 21. It was written by Jason Allardyce, a 40-year-old who was named “Scottish Journalist of the Year” in 2003. His MySpace page states that he likes to go by the name “wolfspider” and that he is based out of Callander. But “wolfspider” is a lonely man. He only has two friends on MySpace: the ever-popular Tom and MySpace UK.
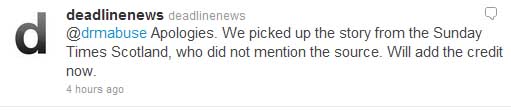
On Easter morning, I knew nothing about Allardyce. A friend had forwarded me this Deadline News report by Peter Laing, in which I recognized quotes identical to my conversation with Ian Rankin on The Bat Segundo Show. The conversation was not accredited. As someone who had investigated the Cooks Source scandal and who remembered the online tarring and feathering, I was appalled that anybody would still consider that ripping off other people’s journalism — even from behind a paywall — would still be okay. But this time, I was on the receiving end for a project that I make little to no money on. For the Rankin show, I had devoted perhaps 25 to 30 hours of my life to reading Rankin’s books, conducting research, interviewing the man for an hour, and mastering the audio. My labor was being exploited. I immediately contacted Laing by email. And on an Easter Sunday, a little less than an hour after I contacted him, he replied back on Twitter:
The Sunday Times? Murdoch’s newspaper? I told people on Twitter about what had happened and asked if anybody could send along the article. And a very friendly pescatarian vegetarian in Scotland going by the name of @SeymourSunshine located the article and photographed it for me.
I transcribed the article. I was stunned to learn that 215 of the 758 words in Jason Allardyce’s article were taken directly and without attribution from my Bat Segundo interview with Ian Rankin. I emailed Alladyce and his editors. And then I discovered that I wasn’t the only one getting played by the wolfspider. An additional 126 words in Allardyce’s article were lifted wholesale and without attribution from two whole paragraphs that Rankin contributed to this Gaby Hinsliff compilation in The Observer from February 13, 2011. To add insult to injury, Allardyce plagiarized a third source, pilfering a good 74 words from this Lisa Zilberpriver piece from World News Australia (January 18, 2010). For all three original pieces that Allardyce has used, a copyright notice was clearly listed on each of the pages.
In other words, Allardyce did not obtain a single original word from his subject for his article.
Ian Rankin was kind enough to confirm with me that nobody from The Times had contacted him. So if we add up the tally, 415 of Allardyce’s 758 words, or 54% of his article, were taken from three separate sources. That’s considerably more words than a famous fair use case here in the States, where The Nation published 300 to 400 words of verbatim quotes from a 500 page Gerald Ford memoir without obtaining permission, was sued, and lost. So that it can all be made clear, here is a breakdown of Allardyce’s liberties (with the unattributed quotes indicated in bold and, for Bat Segundo, the specific times in the program where the words are mentioned):
The writer admitted that Twitter was “taking up more of my life than it should.” [Bat Segundo interview, 27:08-27:09]
He added: “I’ve a kind of addictive personality so I’m always very careful to try to avoid things that can become addictive. [Bat Segundo interview, 27:01-27:06] It’s like a diary. I used to keep a page-a-day diary when I was a kid from the age of 12 till I was 29 and I had to fill up every single page. I couldn’t leave any blank space.” [Bat Segundo interview, 27:49-28:00]
He conquered the diary addiction after moving to America with his wife for six months. [This part is paraphrased from Bat Segundo interview, 28:00-28:30]
“But I use Twitter like it, as a kind of memento mori of everything I have done. [Bat Segundo interview, 28:33-28:37] When I started writing a new book, I made a vow to myself that I wouldn’t go near Twitter until the end of the working day and I kept that up for about three weeks. Then, if I stopped for a cup of coffee, I would check Twitter; stop for lunch, check Twitter. I have to be careful about how many people I follow because, having an addictive personality, I feel the need to read every single tweet on the timeline so if I’m following 300 people that’s potentially 300 people’s tweets I’m reading in any one day…. [Bat Segundo interview, 30:24-30:49]
“I’ve got to go back and read them all. When I wake up in the morning, I’ll go back to the night before and scroll through the night to find out what people were up to.” [Bat Segundo interview, 30:51-31:00]
Rankin said he went through a stage of having a similar addiction to viewing bids on eBay, and that he cannot play computer games because he believes he would be unable to stop, having gone without sleep as a student in order to play them. “It’s insane,” he said. [Bat Segundo interview, plagiarized paraphrase, “I went through a stage of buying vinyl on eBay, buying records…,” 31:02-31:09; “…if I finished browsing eBay…,” 31:10-31:12; direct “It’s insane,” 31:21-31:22]
He recently wrote: “I work from home and work on my own. Twitter connects me to the outside world, and makes it feel as though I’m in a huge, airy office full of funny, well-informed people.
“It gives me instant news, clever jokes, views, and reactions. Fans of my books can contact me, and I can let them know what I’m up to.
“Twitter is also my diary. I can scroll back through my tweets and recall what I was up to on any particular day. I keep in touch with friends make new ones, renew old acquaintances, and sometimes am even gifted ideas for stories. All from my office chair, in 140 characters – which also makes it a fantastic daily exercise in editing and concision.” (The last three paragraphs taken entirely from this Guardian article.)
…
Internet addiction is well recognised, and has even led to the residential treatment programmes in America to help people wean themselves from obsessive use of Twitter, eBay, Facebook, texting and video games. Research published last year suggested that the speed and unpredictability offered by social media stimulates dopamine, which can create an addiction to seeking, rather than finding, contact through them. It added that as more people join in, the scope for overuse grows. (Taken from World News Australia article.)
While it is true that Section 30 of the UK Copyright, Designs, and Patents Act of 1988 specifies a fair dealing exception “for the purpose of criticism or review,” the attribution must contain “a sufficient acknowledgment.” Furthermore, according to English law, there’s very little I can do to stop Allardyce or any other person “reporting current events” from infringing upon copyright provided that “it is accompanied by a sufficient acknowledgment.”
What is a sufficient acknowledgement? Well, unlike much of the American tax codes, you can always count on English law to be concise and thorough. Here’s Section 178 of the CDPA:
“sufficient acknowledgment” mean an acknowledgment identifying the work in question by its title or other description, and identifying the author unless—
(a) in the case of a published work, it is published anonymously;
(b) in the case of an unpublished work, it is not possible for a person to ascertain the identity of the author by reasonable inquiry;
It may very well be a common practice for some UK journalists not to provide attribution. But when they don’t, they are clearly breaking the law. And they are exposing the newspapers and outlets that they write for to considerable legal liability. But more important than such legal propriety, it’s just plain rude and antithetical to the spirit of human togetherness.
But Allardyce’s failure to credit any of his original sources extends far beyond the prospect of fair dealing and fair use. His disingenuous usage could be interpreted as an intent to deceive.
Let’s approach the question form a practical position. Why is attribution important? Well, take this UPI report from September 5, 2010. The UPI quotes Cardinal Keith O’Brien: “Our detailed research into BBC news coverage of Christianity in general and Catholicism in particular, together with a systematic analysis of output from the Catholic church, has revealed a consistent anti-Christian institutional bias.” That’s an extraordinary statement. If you’re at all interested in the many opinions, you’ll want to know where it comes from. And the UPI, because it is a responsible service, notes in its article that The Sunday Telegraph first reported the Cardinal O’Brien quote.
Jason Allardyce, on the other hand, doesn’t make such a distinction when he produces the same quote in his article, and he doesn’t attribute The Telegraph. This causes the Richard Dawkins Foundation (where I found Allardyce’s article, now conveniently hiding behind a paywall) to believe that Allardyce is conducting original reporting. This also causes confusion for the BBC, which erroneously reports that Cardinal O’Brien said these words “in an interview with the Sunday Times.” So Allardyce and The Sunday Times gets credit for a quote that they cut and pasted from another newspaper.
Now let’s say that, several years from now, a historian is looking into biases against religion (or the mythical claims of biases) during the early 21st century. The historian will want to go straight to the original source so that she can ensure that the quote and the context is accurate. But if she has to wade through Allardyce’s misleading attribution, this is going to cause needless work for the historian. Allardyce’s misleading attribution also creates the false impression that the Sunday Times was the central place for that news story.
And because Allardyce has published his “article” in a prominent newspaper, with anyone who reads the article believing that the interview comes from him, there’s very little that I can do to get proper credit or compensation.
I have emailed Allardyce the following terms for resolution:
(a) a public apology, both prominently in print and online, for taking my quotes without asking or attributing;
(b) the issuance of a correction, both prominently in print and online, indicating that the Sunday Times and Jason Allardyce lifted quotes from my radio program, along with a URL directed to my site,
(c) a donation of £500 (as compensation for using my quotes and others without permission or attribution) to Reporters Without Borders.
It’s impossible for me to be entirely objective in this report. I am doing the best that I can to keep a level head. Still, in an age where Arianna Huffington insists that it’s “wrong and offensive to insist that HuffPost is exploiting journalists,” the time has come to stand up against anyone who believes that they can get away from stealing anybody’s labor. If ostensible professionals feel that they are above the law and above the decency of community, then what’s the purpose of their collective existence?
[4/26/11 UPDATE: As of Tuesday afternoon (UK time), Jason Allardyce has not returned my telephone calls and emails.]




 Given this power, the onus on any reviewer is to use it wisely, a wisdom to which there is no finer guide than John Updike and
Given this power, the onus on any reviewer is to use it wisely, a wisdom to which there is no finer guide than John Updike and 
 But on Sunday, de Botton
But on Sunday, de Botton 
