(This is the thirty-ninth entry in the The Modern Library Reading Challenge, an ambitious project to read the entire Modern Library from #100 to #1. Previous entry: The Wapshot Chronicle.)

American history has always been a series of tranquil and joyful moments just before some terrible spill of the cosmic wheelbarrow. The ebb and flow of American life, as it has been and as it always will be, can be perceived as a recurring nightmare: of life, love, felicity, and possibility cast asunder in an unsettling uproar claiming some permanent end to innocence. The hanging chads and butterfly ballots ushering in a presidential monster, only to be eclipsed (and even normalized) sixteen years later by an even greater beast, a lusus naturae even more unhinged and more unsettling. The planes hitting the towers. A pandemic wiping out more than one million Americans. And, of course, the planes that attacked Pearl Harbor and stirred America from its slumber, shoving us into the Second World War.
In our rush to wrap our shivering minds in the warm blanket of nostalgia, as we recall epochs that were seemingly safer and stabler, we often forget that living did not stop and progress was not halted by the deafening clamor of sinister cornets warbling from left field. The best artists have always understood that each deep stab of history’s merciless dirk is answered by reflection and repose, of the battered and bruised emerging triumphantly from these setbacks with resilience and rejuvenation.
We were never like that. We were always like that. The push and pull continues unabated by the “winners” snorting with sow-soaked hubris at the top of the media food chain, with scant regard given to the unsettling totality.
Enter James Jones in 1951, whose massive masterpieces From Here to Eternity and The Thin Red Line are little remembered by anyone under fifty today.
I may very well be the last person under fifty to have signed on for the full James Jones experience. Not even the perspicacious film critic Glenn Kenny finished the Jones doorstopper that he named his thoughtful blog after, but I did.
From Here to Eternity is a peacetime novel bolstered by a trinity of misfits: a former boxer who grew up poor and who invites trouble named Private Robert E. Lee Prewitt (or Prew), a total maniac from Brooklyn who works in the kitchen named Private Angelo Maggio (in other words, a violent and unhinged toxic man who would be immediately canceled, if not arrested on sight, in 2024), and Sergeant Milt Warden, who is having an affair with Karen Holmes, naturally the wife of Captain Dana Holmes, who is the man in charge of G Company. Ther’s also Mess Sergeant Maylon Stark, who, while a minor character in Eternity, I mention here because Jones would take the names and temperaments of these men and reuse them for The Thin Red Line and Whistle, the next two books in his World War II trilogy. So in The Thin Red Line (another Jones masterpiece), Prewitt becomes Witt, Stark changes into Storm, Warden transmutes into Welsh. Then Whistle comes along and Witt is Winch, Prew is Prell, and Stark is Strange. It’s a clever move by Jones to show the interchangeability of certain personality types within the military-industrial complex. Thirty years before Richard Gere famously wailed “I got nowhere else to go!” in An Officer and a Gentleman, Jones understood the painful truth about rudderless men flocking to the military more than anyone.
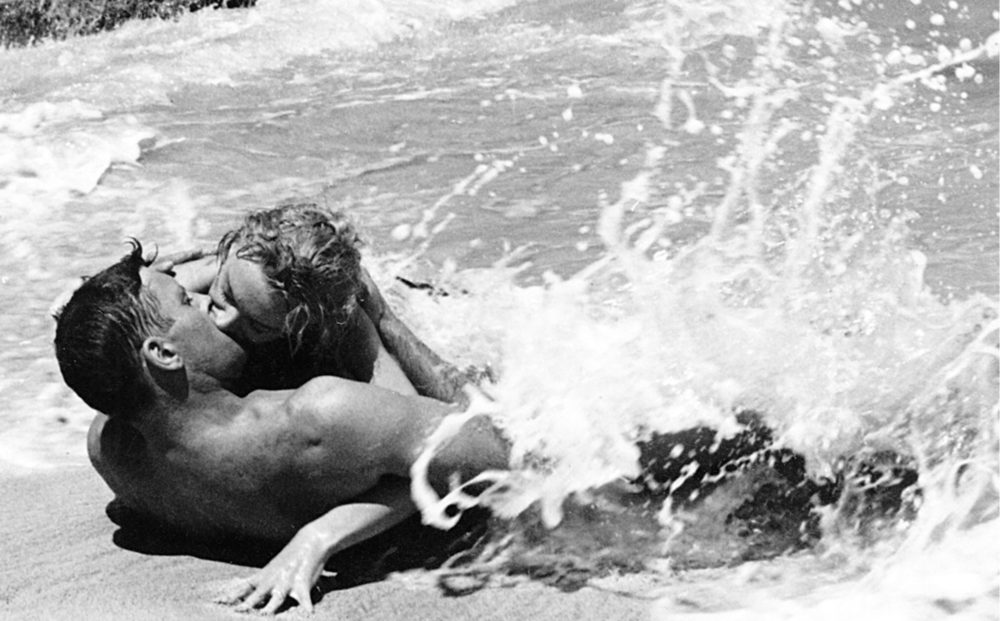
Mention From Here to Eternity to anyone today and they will probably remember (that is, if they do remember) the famous love scene on the beach with Burt Lancaster and Deborah Kerr. But as undeniably romantic as this cinematic moment is, I would say that “Re-Enlistment Blues” probably captures the spirit of the book better than the waves sweeping across gorgeous Hollywood actors (and, hey, I’m not going to deny that Lancaster and Kerr are both incredibly sexy in that scene). I’ve taken the liberty of covering the song, if only to remind the world that it was Jones who wrote the lyrics (since fewer people read these days, why not set the record straight on TikTok?):
You see, Jones rightly perceived the military as an all-encompassing instrument designed to turn fuckups into soldiers through often brutal regimentation. (One can see the full unforgiving horrors against the more libertine and free-thinking men on display in the novel’s brutal chapters in the stockade.) In a December 8, 1939 letter to his brother Jeff, Jones wrote, “I, who am better bred than any of these moronic sergeants, am ordered around by them as if I were a robot, constrained to do their bidding. But I can see their point of view. Nine out of every ten men in this army have no more brains than a three year old. The only way they can learn the manual and the drill commands is by constant repetition. It is pounded into their skulls until it is enveloped by the subconscious mind. The tenth man cannot be excepted. He must be treated the same as the others, even if in time he becomes like them.” A little less than four decades later, Jones would hold to this unsettling truth in his compelling memoir, WWII: A Chronicle of Soldiering: “Men who had been raised to believe, however erroneously, in a certain modicum of individual free-thinking were being taught by loud, fat, devoted sergeants to live as numbers, by the numbers. Clothes that did not fit, when they could see clothes on the shelves that did fit…Being laughed at, insulted, upbraided, held up to ridicule, and fed like pigs at a trough with absolutely no recourse or rights to uphold their treasured individuality before any parent, lover, teacher or tribune. Harassed to rise at five in the morning, harassed to be in bed by nine-thirty at night.”
When From Here to Eternity dropped in 1951, few novelists — with the possible exception of Richard Aldington’s bracingly sardonic Death of a Hero — had dared to betray this unspoken memorandum of understanding. That the truth arrived in fiction six years after the surrender of Japan suggests that it was meant to be confronted, though not in expedient fashion. Three years before, Norman Mailer had merely presented the loneliness and dehumanization of his soldiers. But Jones was prepared to go much further than this, tackling military life with all of its blunt involutions. And it is testament to Jones’s great talent as a writer that Angelo Maggio — the anarchic id at the center of this massive novel — remains an inexplicably poignant figure, a character who charmed Frank Sinatra and, according to his biographer James Kaplan, caused Ol’ Blue Eyes to brood at night speaking his lines from the book and insisting that only he could play the part. (The role salvaged Sinatra’s then flailing career. Sinatra would go onto win an Academy Award for his performance in the 1953 movie. Indeed, it can be plausibly concluded that Sinatra would never have been Sinatra without James Jones. Without Maggio, Sinatra would have ended up as a forgotten crooner, some footnote in 20th century history.)
In stitching all these threads together, Jones was hindered by Scribner’s legal team, which demanded a low-salt version of the authentic soldier dialogue. Only a few years before, Norman Mailer had caved to the censors to get The Naked and the Dead published, using “fug” in lieu of a now commonplace word that one hears frequently from the mouths of enthusiastic teenagers (and causing Dorothy Parker to say, upon being introduced to Mailer, “So you’re the man who can’t spell ‘fuck.'”).
But Jones saw the revision as a creative challenge. In his poignant memoir, James Jones: A Friendship, Willie Morris (who was so tight with Jones that he finished writing the final installment of the World War II trilogy, Whistler, after Jones’s death) got the inside skinny from editor Burroughs Mitchell on how Jones approached this:
It was very hard work; Jim’s ear was so exact that you couldn’t easily remove a word from the dialogue or substitute for it. But he kept doggedly at it, and eventually he began to treat the job as a puzzle, a game, and was delighted with himself when he found solutions. It was characteristic of him, then and afterward, that when an editorial decision was made, a look of anguish would come over his face, he would get up and pace, and finally he’d either accept or say, “I just can’t change that,” looking even more anguished. Finally I reported to Mr. Scribner that we had cut all the fucks we could cut, although not the lawyers’ full quota, and Mr. Scribner cheerfully accepted the situation. That was certainly part of reason why, when Charles Scribner died suddenly, Jim insisted on going to the funeral. He said he knew that Mr. Scribner had been worried about Eternity — but he had gone ahead and published it.
In our present age of sensitivity readers and books being banned or unpublished for spurious reasons, righteous career-destroying ideologues are no less wild-eyed or humorless than their right-wing, anti-art, anti-Critical Race Theory, and casually transphobic counterparts — the kind of regressive dipsticks who wrongly complain about how Russell T. Davies’s new stories for Doctor Who are “too woke” because of pronoun recognition, Davies equipping the TARDIS with a wheelchair ramp (and proudly introducing Ruth Madeley as a disabled UNIT adviser), and the marvelous inclusion of nonbinary characters. But make no mistake: tyranny against expression is not confined to any political affiliation. It is difficult to fathom any modern day corporate publisher who would possess the stones to stick with an author’s artistic vision in the way that Charles Scribner did. (Only four decades after the publication of From Here to Eternity, a gutless vulgarian by the name of Richard E. Snyder, head of Simon & Schuster (which would gobble up the Scribner imprint in 1993), would kibosh the publication of Bret Easton Ellis’s American Psycho, before it was picked up by Vintage, where it would become a huge success (and be reinvented by the inventive Mary Harron as an unforgettable film adaptation mocking toxic masculinity, much as Ariel Levy and John Turturro recently adapted Philip Roth’s Sabbath’s Theatre for the stage in similar fashion). Thankfully, Snyder had the decency to drop dead of heart failure last June after living a long and spineless life lining the coffers of his corporate overlords by publishing “inoffensive” tomes.)
Jones wandered into the writing world a bit too late to get the full Maxwell Perkins treatment (he famously demanded to see Perkins in person as a young writer; Perkins received him and encouraged him, but passed away before he could devote his editorial energies to the entirety of Eternity), but he did have timing on his side, with the valves of permissible dialogue being slowly loosened in the early 1950s, culminating in the opprobrium that Grace Metalious would receive five years later for Peyton Place.
The uncensored version of From Here to Eternity was published by The Dial Press a few years back and, having read both the original and the uncensored versions, I would say that the latter is far superior. There are small differences, such as Maggio allowing a man to go down on him to land some extra cash:
“Oh, sall right. I admit its nothing like a woman. But its something. Besides, old Hal treats me swell. He’s always good for a touch when I’m broke. Five bucks. Ten bucks. Comes in handy the middle of the month.”
But these restored scenes really tell you about the quiet desperation of soldiers. They wait for payday. They augment their meager pay with card games in the latrine. They spend ridiculous amounts of money on sex workers. And they do this because, well, there is nothing else for them. In her incredibly underrated book Stiffed, Susan Faludi documented this problem in the 1990s from a variety of vantage points and concluded that the repugnant patriarchal cues and the way that American culture is conveniently superficial about anxieties that scar lives is equally applicable to men as well as women. And we cannot even begin to solve the underlying problems unless we are honest about all this. As journalists now lose their jobs and sites like The Messenger close their doors and kill their content without notice, it’s incumbent upon us to find the ballsy artists like Jones and stick up for them even when their honest sentiments are offensive or make us uncomfortable. More than five decades after its publication, From Here to Eternity still makes a valiant case for the need to tell and publish the truth.



 You see, I really believe that audio drama, like any artistic form, needs to be written and produced at the highest possible level. But to give this guy some credit, we do have to start somewhere! As someone who has written about 1,400 pages of audio drama and who often labors months over a script until it’s right (as opposed to someone who
You see, I really believe that audio drama, like any artistic form, needs to be written and produced at the highest possible level. But to give this guy some credit, we do have to start somewhere! As someone who has written about 1,400 pages of audio drama and who often labors months over a script until it’s right (as opposed to someone who  Don’t worry too much about your sound design when you’re conceiving your story. You certainly need to remember that this is a medium driven by sound, but, if you’re doing audio drama right, your characters (and thus your actors) will be sharp and lively enough to conjure up a divergent sound environment. It’s absolutely foolhardy and creatively bankrupt to enslave your actors to a soundscape. This represents tyranny, not creative possibility. Actors need to be free to create in a fun and relaxed environment. (In my case, I cook all of my actors breakfast, compensate everyone instantly after recording, and try not to work them more than three hours per recording session.) As perspicacious as you may be, as certain as you may think you are about the rhythm and the delivery, your actors will always have fresh ideas that you haven’t considered. You need to have a script and a recording environment that is committed to your actors first. If you’re looking to be some petty despot, become some small-time corporate overlord. Don’t toil in art. If your actors are hindered by your dictatorial decisions as writer or director, they won’t be able to use their imagination. At all stages, audio drama is a process of collaborative discovery. When you write the script, it’s about creating memorable and three-dimensional characters. When you’re recording with actors, it’s about listening to how an actor interprets the characters and shaping the scene together with openness, trust, and experimentation. Then, when you’re putting together the rough edit (dialogue only), you have yet another stage of discovery. The actors have given you all that you need. You’ll be able to imagine where they are in a room, what they’re doing, and what else might be with them. From here, you start to form the sound design. Worldbuilding always comes from human investigation. And if you’re fully committed to the human, then your instinctive imagination will be able to devise a unique aural environment.
Don’t worry too much about your sound design when you’re conceiving your story. You certainly need to remember that this is a medium driven by sound, but, if you’re doing audio drama right, your characters (and thus your actors) will be sharp and lively enough to conjure up a divergent sound environment. It’s absolutely foolhardy and creatively bankrupt to enslave your actors to a soundscape. This represents tyranny, not creative possibility. Actors need to be free to create in a fun and relaxed environment. (In my case, I cook all of my actors breakfast, compensate everyone instantly after recording, and try not to work them more than three hours per recording session.) As perspicacious as you may be, as certain as you may think you are about the rhythm and the delivery, your actors will always have fresh ideas that you haven’t considered. You need to have a script and a recording environment that is committed to your actors first. If you’re looking to be some petty despot, become some small-time corporate overlord. Don’t toil in art. If your actors are hindered by your dictatorial decisions as writer or director, they won’t be able to use their imagination. At all stages, audio drama is a process of collaborative discovery. When you write the script, it’s about creating memorable and three-dimensional characters. When you’re recording with actors, it’s about listening to how an actor interprets the characters and shaping the scene together with openness, trust, and experimentation. Then, when you’re putting together the rough edit (dialogue only), you have yet another stage of discovery. The actors have given you all that you need. You’ll be able to imagine where they are in a room, what they’re doing, and what else might be with them. From here, you start to form the sound design. Worldbuilding always comes from human investigation. And if you’re fully committed to the human, then your instinctive imagination will be able to devise a unique aural environment. But to get to this place, you need to have characters who are unusual and who contain subtlety, depth, and detailed background. What kind of family did they have? Are they optimistic or moody? What was their most painful experience? Their happiest? Are they passionate about anything? If you’re stuck, you could always try revisiting some personal experience. For
But to get to this place, you need to have characters who are unusual and who contain subtlety, depth, and detailed background. What kind of family did they have? Are they optimistic or moody? What was their most painful experience? Their happiest? Are they passionate about anything? If you’re stuck, you could always try revisiting some personal experience. For  The misguided dramatist also reveals how pedestrian and unambitious he is in his storytelling when he tells you that you shouldn’t have more than four separate voices in a scene. This is only a problem if, like the misguided dramatist, you are too reliant upon seemingly clever ideas and don’t know how to write recognizable characters. If your characters are dimensional, then your audience will be able to follow the story. But you can also have your characters forget the names of the people who they are with so that you have an opportunity to remind your audience who they are. There are, after all, few people who attend a party and who manage to remember everybody’s first names. This expositional move doubles as a touch of realism and a subtle way of helping your audience keep track of a very large cast. Don’t squelch your ambition! If the dialogue is natural and the rhythm reflects real human conversation, then this will also help your audience lock into the narrative.
The misguided dramatist also reveals how pedestrian and unambitious he is in his storytelling when he tells you that you shouldn’t have more than four separate voices in a scene. This is only a problem if, like the misguided dramatist, you are too reliant upon seemingly clever ideas and don’t know how to write recognizable characters. If your characters are dimensional, then your audience will be able to follow the story. But you can also have your characters forget the names of the people who they are with so that you have an opportunity to remind your audience who they are. There are, after all, few people who attend a party and who manage to remember everybody’s first names. This expositional move doubles as a touch of realism and a subtle way of helping your audience keep track of a very large cast. Don’t squelch your ambition! If the dialogue is natural and the rhythm reflects real human conversation, then this will also help your audience lock into the narrative.  Once again, the misguided dramatist lacks the ability to comprehend how an audience vicariously relates to an audio drama. You can do kissing in audio drama. I’ve included it in
Once again, the misguided dramatist lacks the ability to comprehend how an audience vicariously relates to an audio drama. You can do kissing in audio drama. I’ve included it in  You’re not going to please everyone. So why spend so much time worrying about it? There are incredibly talented and impeccably kind people who produce beloved audio dramas and even they receive hate mail and vicious criticism. Critics, by and large, are far less useful than the honest and experienced people you have in your corner who understand both you and the hard work that goes into making audio drama. You need to be surrounded by beta readers and beta listeners who will not bullshit you. Your duty as an artist is to not give into the often insane demands of rabid fans (much as one very popular audio drama did a few years ago, forcing this truly terrific show to ignobly close its doors) and to concentrate on putting out your best work. The real crowd, your truly loyal listeners and the ones who you actually learn from, will trust you enough to continue with the journey. The same goes with your actors. I took a huge risk on a Season 2 script. And I was incredibly surprised, humbled, and honored when the actors were crazy about it and told me what a thrilling twist it was and brought their A game when we recorded. You have a duty to keep on growing. Keep in mind that critics, especially the small-time character assassins on Twitter driven by acute resentment, reflect a vocal minority. You’re also probably never going to get a TV deal. So why chase that kind of outsize success? Besides, it’s far more rewarding to tell stories entirely on your own terms. If the work is good and you treat people well, you will attract very talented actors. And they in turn will tell their actor friends about how much fun you are to work with. But if you tell the same story over and over again, or you aren’t sufficiently answering the many questions you’ve set up, chances are you’ll be pulling a Damon Lindelof. And everyone will rightfully ding you for writing a lazy and inane climax.
You’re not going to please everyone. So why spend so much time worrying about it? There are incredibly talented and impeccably kind people who produce beloved audio dramas and even they receive hate mail and vicious criticism. Critics, by and large, are far less useful than the honest and experienced people you have in your corner who understand both you and the hard work that goes into making audio drama. You need to be surrounded by beta readers and beta listeners who will not bullshit you. Your duty as an artist is to not give into the often insane demands of rabid fans (much as one very popular audio drama did a few years ago, forcing this truly terrific show to ignobly close its doors) and to concentrate on putting out your best work. The real crowd, your truly loyal listeners and the ones who you actually learn from, will trust you enough to continue with the journey. The same goes with your actors. I took a huge risk on a Season 2 script. And I was incredibly surprised, humbled, and honored when the actors were crazy about it and told me what a thrilling twist it was and brought their A game when we recorded. You have a duty to keep on growing. Keep in mind that critics, especially the small-time character assassins on Twitter driven by acute resentment, reflect a vocal minority. You’re also probably never going to get a TV deal. So why chase that kind of outsize success? Besides, it’s far more rewarding to tell stories entirely on your own terms. If the work is good and you treat people well, you will attract very talented actors. And they in turn will tell their actor friends about how much fun you are to work with. But if you tell the same story over and over again, or you aren’t sufficiently answering the many questions you’ve set up, chances are you’ll be pulling a Damon Lindelof. And everyone will rightfully ding you for writing a lazy and inane climax.









