(This is the twenty-eighth entry in The Modern Library Nonfiction Challenge, an ambitious project to read and write about the Modern Library Nonfiction books from #100 to #1. There is also The Modern Library Reading Challenge, a fiction-based counterpart to this list. Previous entry: James Joyce.)
 As I write these words — some eight months before a fateful presidential election threatens to steer my nation into a theocratic hellscape that will permanently erode many of the liberties and freedoms I have been humbled to partake in for cnearly fifty years — the tireless researchers at PRII inform me that Christian nationalism has substantive support in all fifty states (with the exception of California, New York, and Virginia — in which 75% remain skeptics or outright reject it), the Pew Research Center reports that 45% of Americans believe that our democratic republic should be “a Christian nation,” and 55% of Latino Protestants support Christian nationalism. Blind zealotry, even with white supremacy mixed into the sickening formula, comes in many colors.
As I write these words — some eight months before a fateful presidential election threatens to steer my nation into a theocratic hellscape that will permanently erode many of the liberties and freedoms I have been humbled to partake in for cnearly fifty years — the tireless researchers at PRII inform me that Christian nationalism has substantive support in all fifty states (with the exception of California, New York, and Virginia — in which 75% remain skeptics or outright reject it), the Pew Research Center reports that 45% of Americans believe that our democratic republic should be “a Christian nation,” and 55% of Latino Protestants support Christian nationalism. Blind zealotry, even with white supremacy mixed into the sickening formula, comes in many colors.
Undoubtedly, many of these hayseed fanatics are easily manipulated and illiterate. They conveniently overlook the “love thy neighbor” ethos from Western civilization’s best known zombie in favor of a greater affinity for the limitless imbecility of zealous violence and tyranny, falsely believing themselves to be misunderstood rebels living in a new Roman Empire — this as the very institutional framework continues to uphold their right to yap and bellow in hateful and discriminatory terms as they line the pockets of wealthy telegenic carpetbaggers like Joel Osteen. They lead campaigns to ban books and to deracinate vital areas of knowledge from schools which offend their delicate and autocratically vanilla sensibilities. While the Book of Luke informs us that Christ asked us to “love and pray for our enemies,” you will find these unremarkable lemmings keeping their traps shut as trans kids commit suicide or another maniac massacres dozens in the week’s latest mass shooting. (Unable to summon true comity for anyone who deviates from their ugly and crudely formed politics, right-wing statesmen have substituted “love” for “thoughts,” presumably so they can show up to church on Sunday with a “clean” Christian conscience — even though they do nothing to curb this malignant cancer and care no more for these victims than any garden-variety sociopath.)
It has frequently been observed that atheists like myself know the Bible better than these monomoniacal morons. I have often been surprised by how easy it is to thoroughly rebut some born-again loser based on a singular reading of the King James more than twenty years ago and my apparent recall of specific passages that are well outside the soft and useless hippocampi of my hopelessly dim opponents. It never occurs to Christians to question their faith or even to comprehend (much less read) the very words they purport to uphold in their everyday living. And it certainly wouldn’t occur to them to consider that, much like any moment in history, the narrative and the very belief structure upholding this nonsense was written by the winners, by those who spent the majority of their lives silencing (and even murdering) anyone who offered perfectly reasonable questions about a man who rose from the dead.
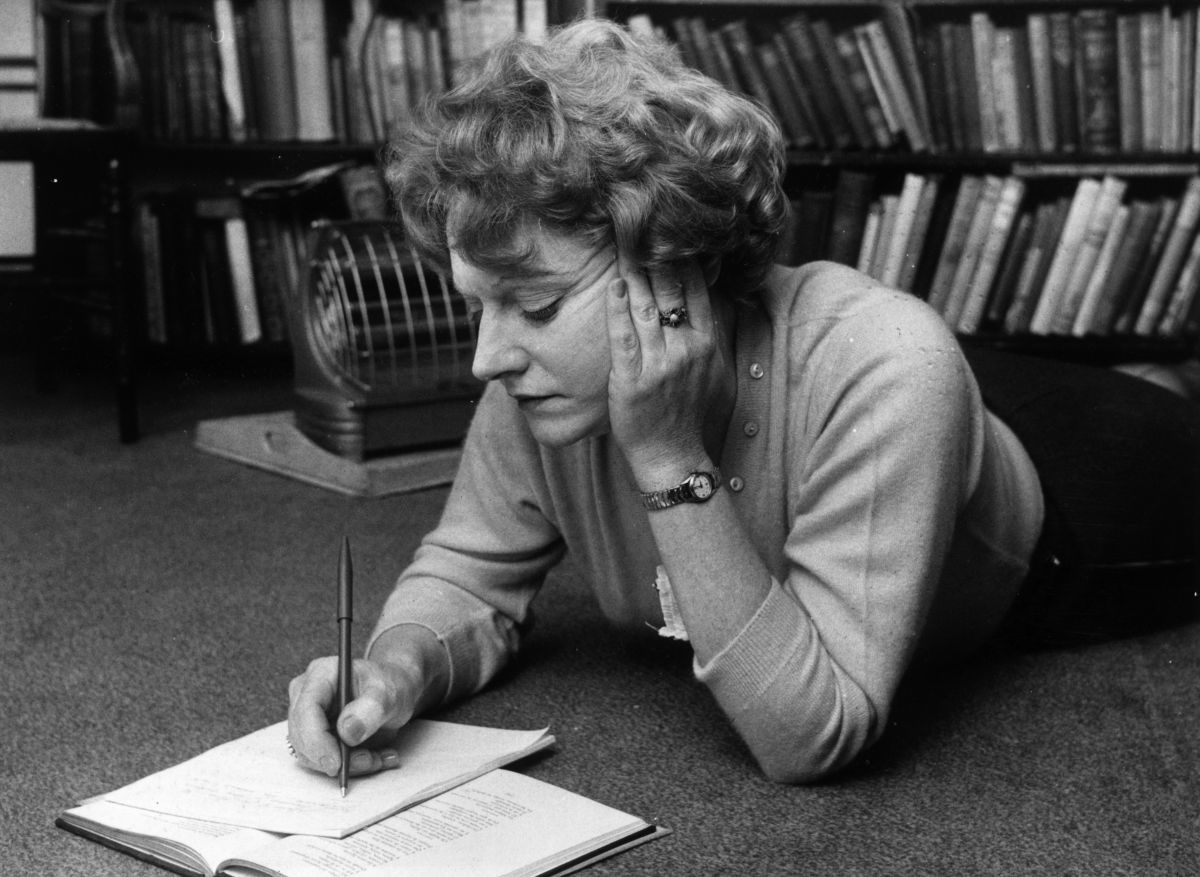
Elaine Pagels’s excellent book, The Gnostic Gospels, is an equitable study of the many Gnostic sects that dared to question the Christian status quo. Indeed, had not the 52 treatises been discovered in Nag Hammadi in 1945, there is a good chance that many of us who tirelessly call out bullshit on all fronts would have lacked a far more seminal faith than one in Christ — namely, a boundless pride in our ancestors practicing the vital art of critical thinking.
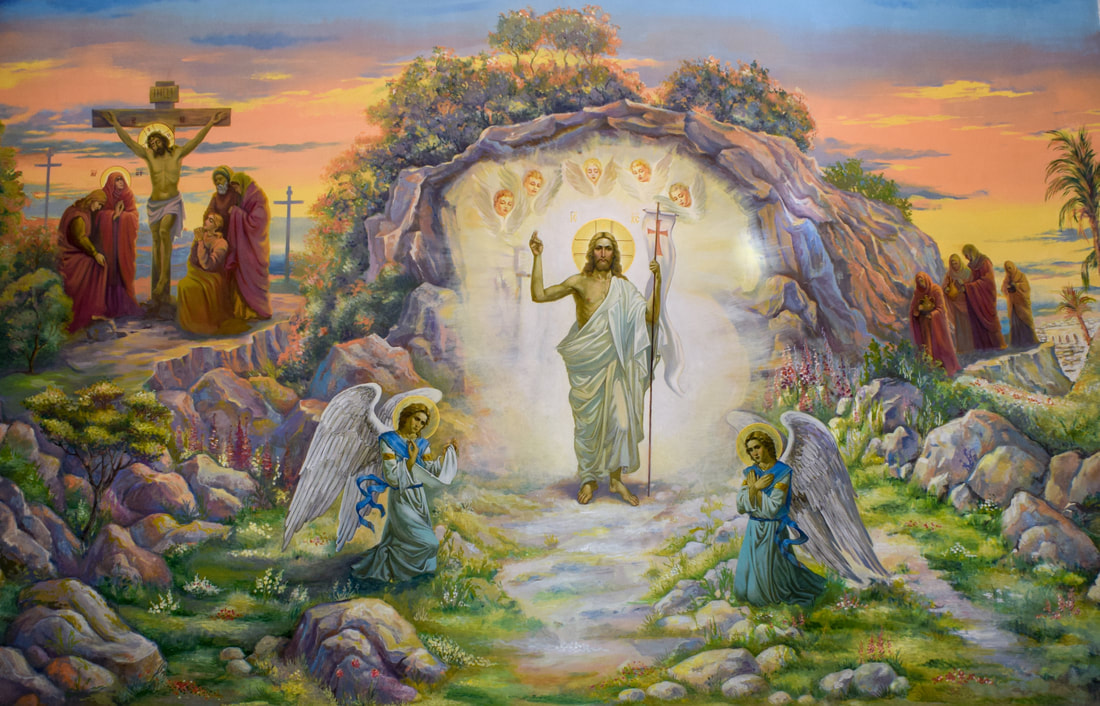
The orthodox position of the Resurrection, as defined by Tertullian, is quite clear. Jesus Christ rose from the dead with full corporeal gusto. It was “this flesh, suffused with blood, built up with bones, interwoven with nerves, entwined with veins” (one might add “consummated with claptrap” and “molded with malarkey” to this laundry list). Tertullian further adds, “it must be believed, because it is absurd!” And, look, I’d like to believe in kaiju secretly emerging from the oceans to stomp on every megachurch from here to Alpharetta, Georgia, but I have confined my love for absurdity to my deviant imagination and my performative antics on TikTok.
What’s especially astonishing about Tertullian is how literal he is. The New Testament is ripe with stories in which Jesus’s disciples are invited to prod and touch the newly reanimated corpse. (There is curiously nothing in the Bible in which anyone asks Jesus about why he doesn’t carry the pungent smell of the dead or how the bearded wonder managed to rid himself of all the maggots gnawing at his decaying flesh.) And yet Pagels points out that not every story within the New Testament aligns with Tertullian’s “my way or the highway” interpretation of full-fledged concrete return. Acts 9:3-4 informs us that Christ’s Resurrection is merely “a light from heaven” with a voice. Acts 22:9 even points out that some observed the light, but ‘heard not the voice that spake to me.” And if that’s the case, would Tertullian have declared the Apostles heretics? In Acts, Christ’s “return” sounds very much like a low-rent Vegas act without a PA system.
And that’s just in the Bible, folks! I haven’t even snapped my fingers to summon the Gnostics on stage. Depending upon what part of the Bible you read, it is either Peter or Mary Magdalene who first sees Christ rise from the dead. Paul tells us that Christ said hello to five hundred people all at once. And if we take that literally, any of us could now do the same thing on social media. Pagels informs us that from the second century onward, “orthodox churches developed the view that only certain resurrection appearances actually conferred authority on those who received them.” And just like that, the manner in which you contend with Christ’s reappearance isn’t all that different from telling the right story to some bouncer on a Saturday night to slip past the velvet rope!
Believe in the power of this two-bit magician and the terms of the deal, as set up by Luke, are as follows: Christ returned from the dead, walked the earth for forty days, and then rose to the heavens in a bright coruscating light. This may not have the razzle-dazzle of Cirque du Soleil, but it is a belief that has nevertheless been swallowed whole and without question by generations of gullible rubes.
The Gnostics were the first to call this “the faith of fools.” In The Acts of John, one of the rare Gnostic texts that survived before Nag Hammadi in fragmented form, John offers the completely reasonable argument that, because Christ did not leave any footprints, he could not possibly be human, but spiritual. The Gnostics clearly had a more sophisticated interpretation of the Resurrection: it was not the literal observation of Christ’s Resurrection that counted, but the spiritual meaning behind it. But the underlying facts didn’t matter nearly as much as winning over the authorities who conferred you with a position of trust:
Consider the political implications of the Gospel of Mary: Peter and Andrew, here representing the leaders of the orthodox group, accuse Mary — the gnostic — of pretending to have seen the Lord in order to justify the strange ideas, fictions, and lies she invents and attributes to divine inspiration. Mary lacks the proper credentials for leadership, from the orthodox viewpoint: she is not one of the ‘twelve.’ But as Mary stands up to Peter, so the gnostics who take her as their prototype challenge the authority of those priests and bishops who claim to be Peter’s successors.
It thus became necessary for the Gnostics to expand authority to those who stood outside the Twelve. Some Gnostics were generous enough to ascribe VIP treatment to the Disciples, claiming that they had received the kind of custom vision that is a bit like the gift you receive nine months after you donate to a Kickstarter campaign. But as you can imagine, all this resulted in many elbowing their way into a vicious power grab over which interpretation of the Resurrection represented the “true” belief. And there was another important consideration. If Christ himself served as the truest source of spiritual authority, who then would be the authority in the years after his crucifixion and his “Hey there, baby!” sojurn from the great beyond?
The more bellicose strains of Christianity continue to endure in large part because a belief in Christ conveniently allows you to disguise your own sinister lunges for power. Enter Pope Clement I, who was arguably the first significantly ruthless monster who saw an opportunity. Clement insisted that, in the absence of his august presence, God delegates his authority to the “rulers and leaders on earth.” Naturally, these “rulers and leaders” were bishops, deacons, and priests. And if you didn’t bend at the knee to these sham practitioners, then Clement stated, with his great gift for speaking without nuance, that you would receive the death penalty.
Of course, this raises the question of whom you can trust within the church: an issue that has become evermore important given the decades of sexual abuse carried out by men of the cloth within the Catholic Church. A bloodthirsty fellow by the name of Irenaeus succeeded in widening the divide between orthodoxy and the Gnostics by suggesting that any interpretation existing outside Clement’s stern terms was not only heretical, but originated from Satan himself, thus paving the way for Christians to denounce any belief or behavior they disagreed with as “Satanic” over the next two thousand years. Over the years, they proceeded to execute innocent women in Salem and imagine Satanic messages in records.
These developments spelled trouble for the poor Gnostics. Within a few centuries, their texts were buried and destroyed. Their reasonable questions and liberal interpretations became casus belli to string them up. The Christians had the good sense to market themselves as victims persecuted by the Roman Empire and they began to realize sometime in the second century that pointing out how Christians suffered was a great draw for new acolytes. (Eighteen centuries later, Israel would employ the same tactic: use the suffering from the Holocaust to recruit Zionists, where they could then justify the seizure of Palestinian land and the mass-murdering of children on the Gaza Strip.) All this is a pity. Because the Gnostics were often far more interesting in their radicalism and their creative liturgical analysis than what we find in the so-called Holy Book. Consider The Gospel of Philip‘s inventive spin on the virgin birth. How can the Spirit be both Virgin and Mother? By a union between the Father of All and the Holy Spirit. And unlike the Christians, The Gospel of Peter ascribed a third quality to the Divine Mother (the first two being the Silence and the Holy Spirit): Wisdom, clearly delineated as a feminine power.
It is a testament to Christianity’s enduring evil that few people listen to the Gnostics in the twenty-first century. But if their reasonable transposition of literal interpretation to metaphor had become the more dominant text, it is quite possible that the millions of nonbelievers who died during the Crusades might have survived and that the present plague of Christian nationalism, which remains highly dangerous and ubiquitous in our dystopian epoch, might have nestled into the less injurious category of “optional only.”
{Next Up! William H. McNeill’s The Rise of the West!)
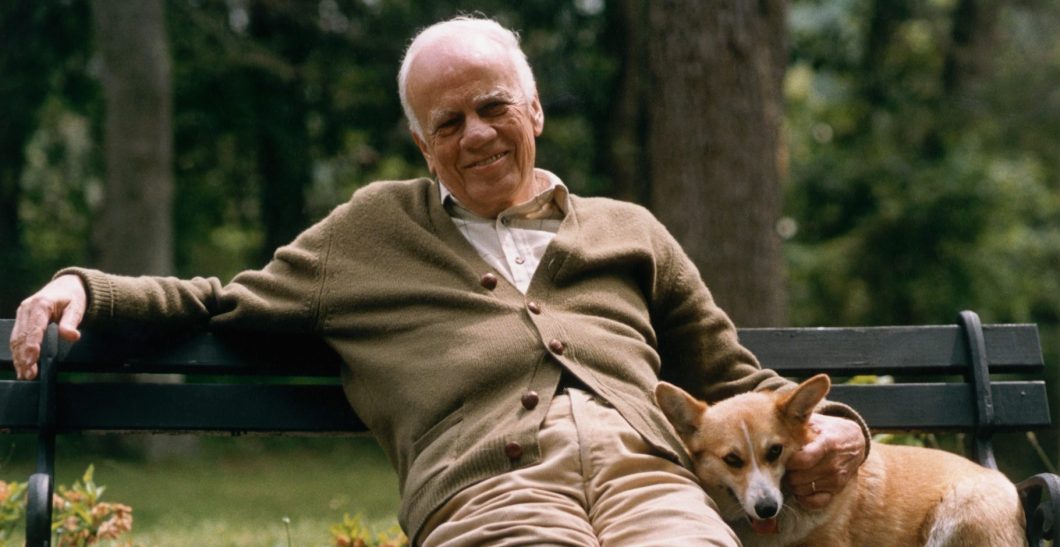
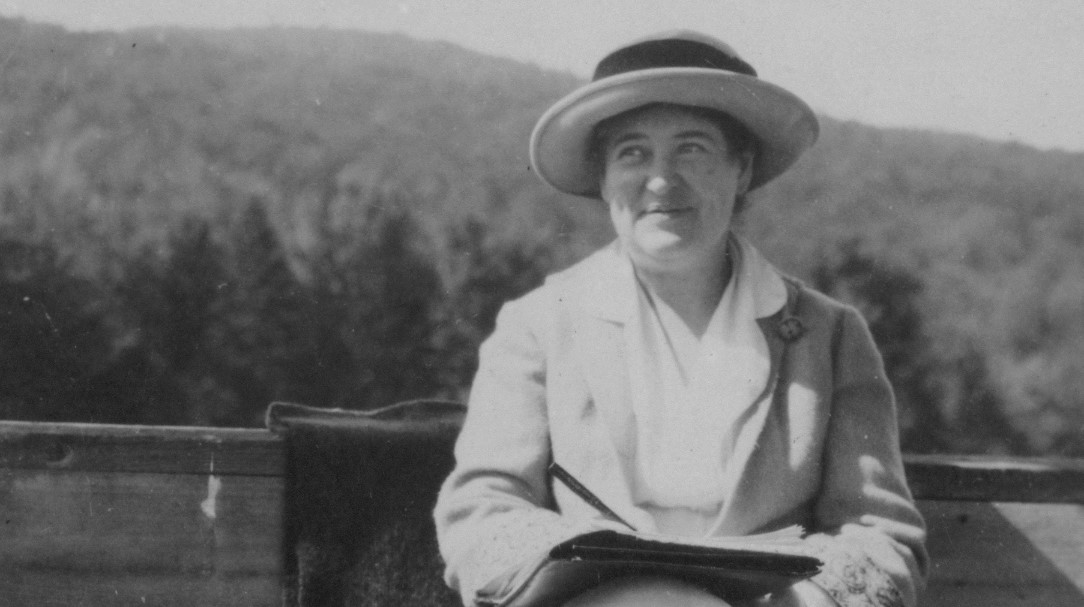
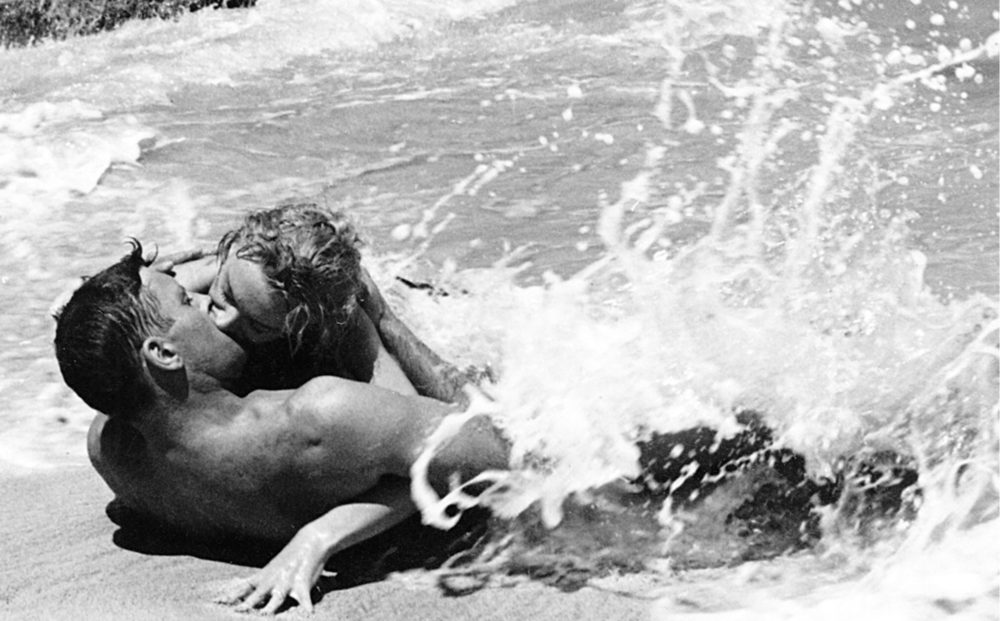
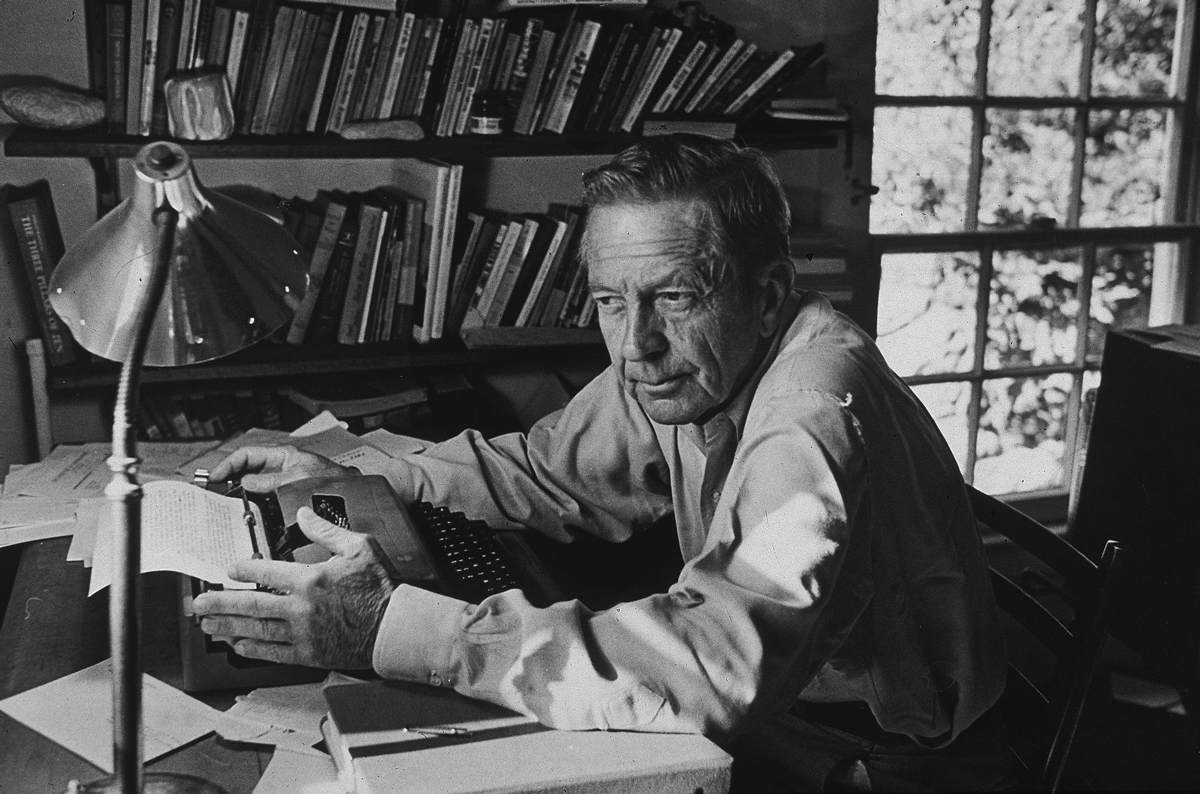







 Despite focusing almost exclusively on the upper and middle classes in his fiction, John Cheever was that rare New Yorker regular whose short stories never came across as off-puttingly imperious, superficially urbane, or especially pretentious (although he did don a mannered Mid-Atlantic accent for his television appearances; his
Despite focusing almost exclusively on the upper and middle classes in his fiction, John Cheever was that rare New Yorker regular whose short stories never came across as off-puttingly imperious, superficially urbane, or especially pretentious (although he did don a mannered Mid-Atlantic accent for his television appearances; his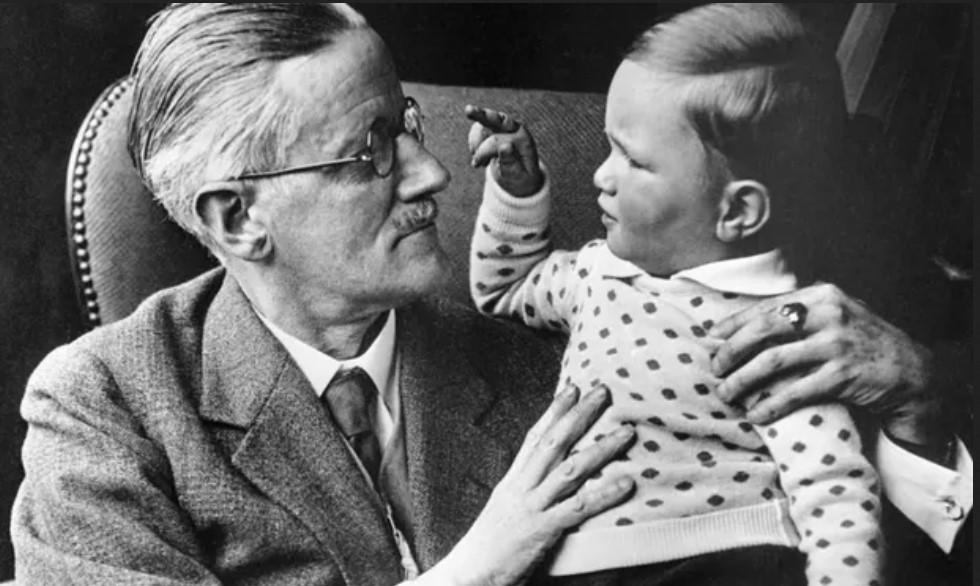 
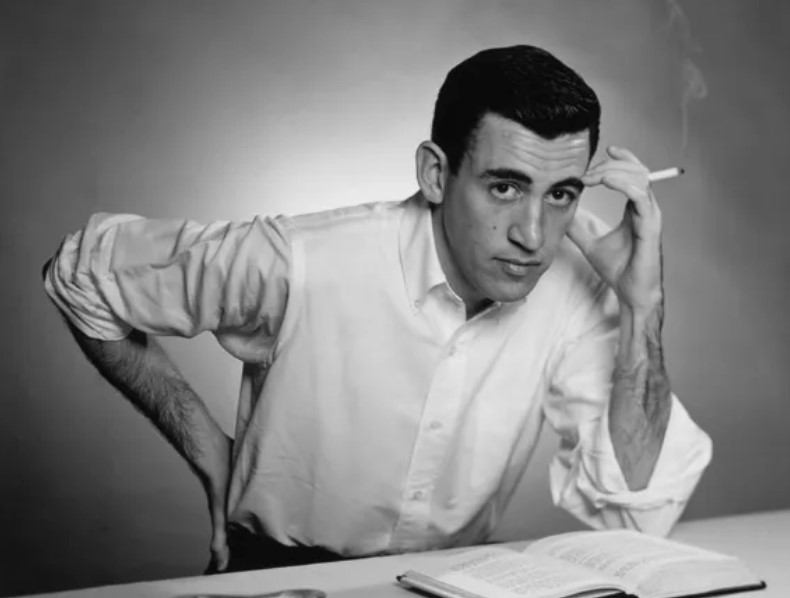

 Like many semi-literate members of my generation, I first read The Catcher in the Rye at the age of fifteen, following the ethereal rites and cadences of older kids turned on by the same seductive anthem to nonconformity. At that angsty teenage time in my life, Holden Caulfield appealed to my rebellious and anti-authoritarian streak. This reaction, in and of itself, is not especially unusual. Salinger has continued to be assigned to high school English curricula in large part because you can inveigle kids into reading by making the titles forbidden. (Witness how Art Spiegelman’s Maus
Like many semi-literate members of my generation, I first read The Catcher in the Rye at the age of fifteen, following the ethereal rites and cadences of older kids turned on by the same seductive anthem to nonconformity. At that angsty teenage time in my life, Holden Caulfield appealed to my rebellious and anti-authoritarian streak. This reaction, in and of itself, is not especially unusual. Salinger has continued to be assigned to high school English curricula in large part because you can inveigle kids into reading by making the titles forbidden. (Witness how Art Spiegelman’s Maus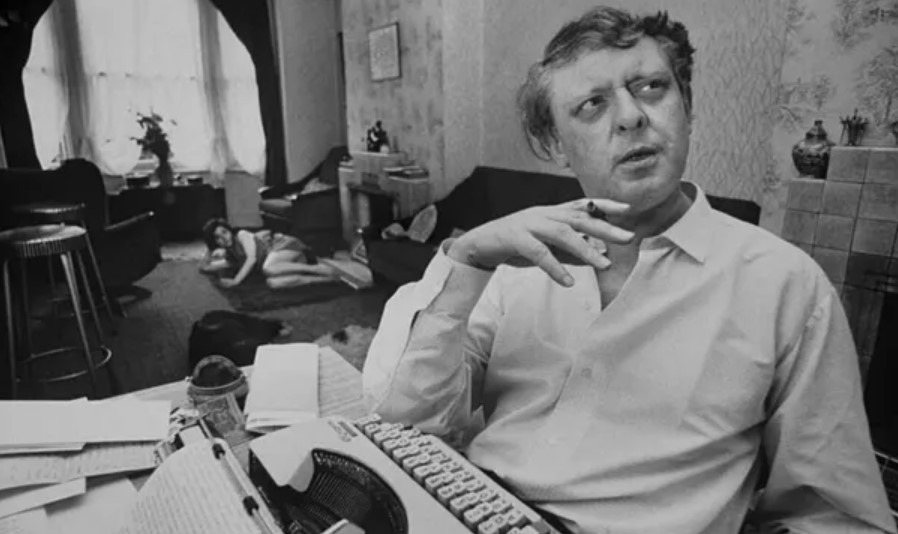 
 It’s become quite fashionable to bash the ridiculously prolific and mock pompous Mancunian with the combover. Never mind that anyone with a remote familiarity for how theatre comes together recognizes that Anthony Burgess perfected a magnetic if abrasive persona, frequently appearing on television
It’s become quite fashionable to bash the ridiculously prolific and mock pompous Mancunian with the combover. Never mind that anyone with a remote familiarity for how theatre comes together recognizes that Anthony Burgess perfected a magnetic if abrasive persona, frequently appearing on television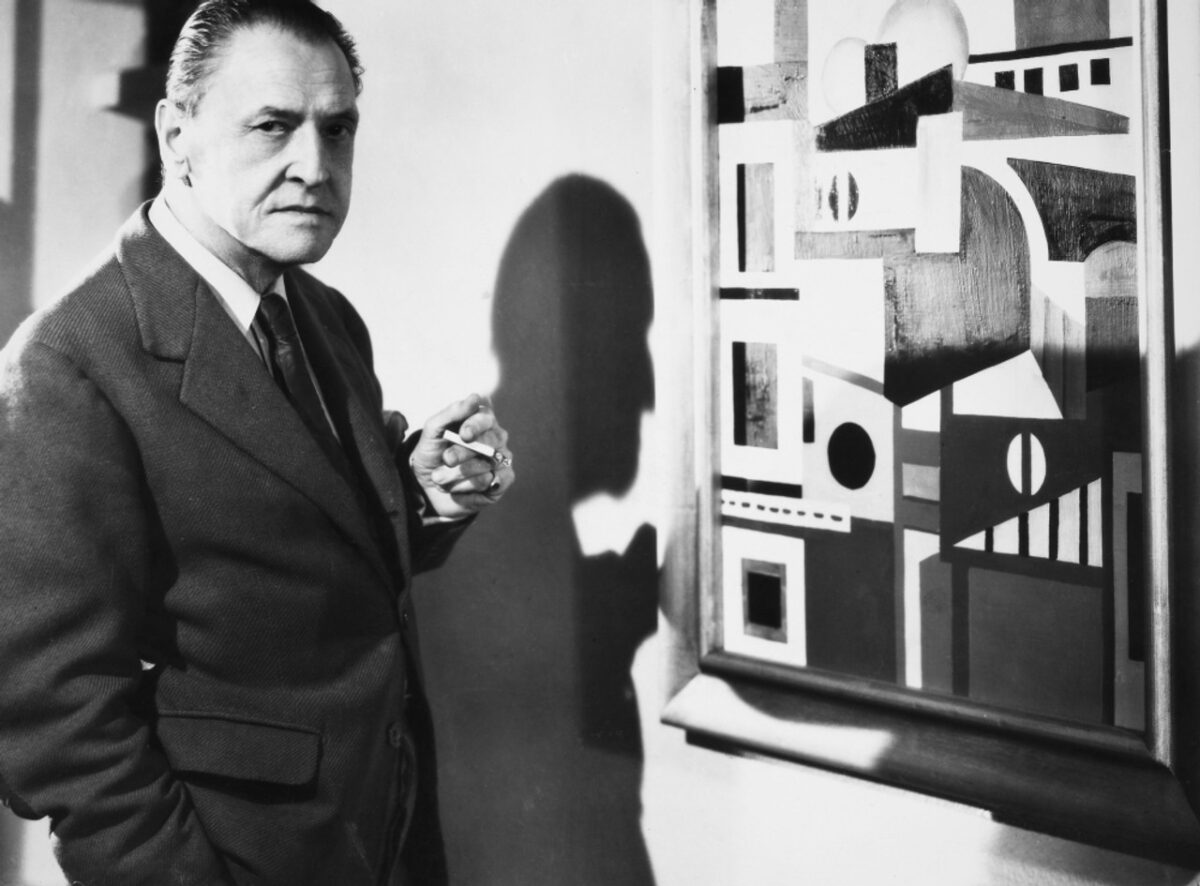 
 William Somerset Maugham was a largely gloomy man who just wanted to be loved. And because Maugaham was constitutionally incapable of behaving in the manner of Sally Field accepting her Oscar (and was frequently self-deprecatory), he often wasn’t. It certainly did not help that he was closeted, emo as fuck, fiercely protective of his private life, tight-lipped about his inexorable agony, and reported by many of his acquaintances and admirers as emotionally detached (although he did commit many quiet acts of generosity, including building up a library at The King’s School in Canterbury, where the ashes of Ashenden’s creator were eventually scattered). He frequently quipped that he stood in the first row of second-rate writers, almost to steel himself against the effusive and well-deserved reception he received for his considerable literary accomplishments. The Moon and Sixpence, Cakes and Ale, and The Painted Veil remain remarkably vivacious and salacious for their time and are still eminently readable today.
William Somerset Maugham was a largely gloomy man who just wanted to be loved. And because Maugaham was constitutionally incapable of behaving in the manner of Sally Field accepting her Oscar (and was frequently self-deprecatory), he often wasn’t. It certainly did not help that he was closeted, emo as fuck, fiercely protective of his private life, tight-lipped about his inexorable agony, and reported by many of his acquaintances and admirers as emotionally detached (although he did commit many quiet acts of generosity, including building up a library at The King’s School in Canterbury, where the ashes of Ashenden’s creator were eventually scattered). He frequently quipped that he stood in the first row of second-rate writers, almost to steel himself against the effusive and well-deserved reception he received for his considerable literary accomplishments. The Moon and Sixpence, Cakes and Ale, and The Painted Veil remain remarkably vivacious and salacious for their time and are still eminently readable today. 
 It can’t be an accident that the wildly underrated Julian MacLaren-Ross skewered the idea of reading Conrad as an upwardly mobile class aspiration in Of Love and Hunger. In Frog, Stephen Dixon took the piss out of Conrad along these lines as well. Indeed, slagging off Conrad seems to be a common trait among many of my literary Bohemian heroes. And I do need to heed them. I feel and trust their instincts. It’s almost as if we’re told that we should simply accept that Conrad is a great writer who changed the course of literature (and he did) even as we pretend that he isn’t ancient and hoary and horribly regressive. When I confessed my reluctance to reread Heart of Darkness to a few friends, they told me, “Well, it’s only a hundred pages.” Which suggested very strongly that nobody really wants to read Conrad anymore. He doesn’t pop out at you like Joyce or Faulkner or Nabokov or even Lawrence. And, to tell you the truth, I would much rather reread
It can’t be an accident that the wildly underrated Julian MacLaren-Ross skewered the idea of reading Conrad as an upwardly mobile class aspiration in Of Love and Hunger. In Frog, Stephen Dixon took the piss out of Conrad along these lines as well. Indeed, slagging off Conrad seems to be a common trait among many of my literary Bohemian heroes. And I do need to heed them. I feel and trust their instincts. It’s almost as if we’re told that we should simply accept that Conrad is a great writer who changed the course of literature (and he did) even as we pretend that he isn’t ancient and hoary and horribly regressive. When I confessed my reluctance to reread Heart of Darkness to a few friends, they told me, “Well, it’s only a hundred pages.” Which suggested very strongly that nobody really wants to read Conrad anymore. He doesn’t pop out at you like Joyce or Faulkner or Nabokov or even Lawrence. And, to tell you the truth, I would much rather reread 


 Our universe has become more hopelessly transactional. Vile narcissists with limitless greed and an absence of smarts and empathy have taken over the landscape with their blunt bullhorns. At every socioeconomic level, you will find a plurality of mercenaries who will push any bright and promising head beneath the waterline with ruthless cruelty. Perhaps I’m finally understanding, at an embarrassingly late age, just how commonplace such self-serving treachery is in our world. But what’s the alternative? Cynicism? At times, I have a sense of humor that is darker than the nightscape above the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory, but no thanks. I’ve always been a cautious optimist with a healthy handle on reality, but I still detest this state of affairs. I will still speak out vociferously against it and fight the business-as-usual cowards who uphold this great sham known as the status quo at any personal cost. I stump for the outliers and the misfits. The people who have authentic and vital voices. I don’t care who they are or where they come from. I will stick up for the gas station attendants and the baristas. I will listen to their full stories rather than judge them from a fleeting glance or a superficial and supercilious position. I despise bullies and opportunists. I believe in affording everyone basic dignity. I believe that everyone has it within them to grow and to learn and that inquisitive efforts should never be mocked, especially when genuine curiosity is now in such short supply. Reprobates who use their positions of power to denigrate the marginalized and the underprivileged are scumbags who need to be fought and, if necessary, destroyed.
Our universe has become more hopelessly transactional. Vile narcissists with limitless greed and an absence of smarts and empathy have taken over the landscape with their blunt bullhorns. At every socioeconomic level, you will find a plurality of mercenaries who will push any bright and promising head beneath the waterline with ruthless cruelty. Perhaps I’m finally understanding, at an embarrassingly late age, just how commonplace such self-serving treachery is in our world. But what’s the alternative? Cynicism? At times, I have a sense of humor that is darker than the nightscape above the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory, but no thanks. I’ve always been a cautious optimist with a healthy handle on reality, but I still detest this state of affairs. I will still speak out vociferously against it and fight the business-as-usual cowards who uphold this great sham known as the status quo at any personal cost. I stump for the outliers and the misfits. The people who have authentic and vital voices. I don’t care who they are or where they come from. I will stick up for the gas station attendants and the baristas. I will listen to their full stories rather than judge them from a fleeting glance or a superficial and supercilious position. I despise bullies and opportunists. I believe in affording everyone basic dignity. I believe that everyone has it within them to grow and to learn and that inquisitive efforts should never be mocked, especially when genuine curiosity is now in such short supply. Reprobates who use their positions of power to denigrate the marginalized and the underprivileged are scumbags who need to be fought and, if necessary, destroyed.
 Of the four illustrious figures cannonaded in Eminent Victorians, Florence Nightingale somehow evaded the relentless reports of Lytton Strachey’s hard-hitting flintlocks. Strachey, of course, was constitutionally incapable of entirely refraining from his bloodthirsty barbs, yet even he could not find it within himself to stick his dirk into “the delicate maiden of high degree who threw aside the pleasures of a life of ease to succor the afflicted.” Despite this rare backpedaling from an acerbic male tyrant, Nightingale was belittled, demeaned, and vitiated for many decades by do-nothings who lacked her brash initiative and who were dispossessed of the ability to match her bold moves and her indefatigable logistical acumen, which were likely fueled by
Of the four illustrious figures cannonaded in Eminent Victorians, Florence Nightingale somehow evaded the relentless reports of Lytton Strachey’s hard-hitting flintlocks. Strachey, of course, was constitutionally incapable of entirely refraining from his bloodthirsty barbs, yet even he could not find it within himself to stick his dirk into “the delicate maiden of high degree who threw aside the pleasures of a life of ease to succor the afflicted.” Despite this rare backpedaling from an acerbic male tyrant, Nightingale was belittled, demeaned, and vitiated for many decades by do-nothings who lacked her brash initiative and who were dispossessed of the ability to match her bold moves and her indefatigable logistical acumen, which were likely fueled by 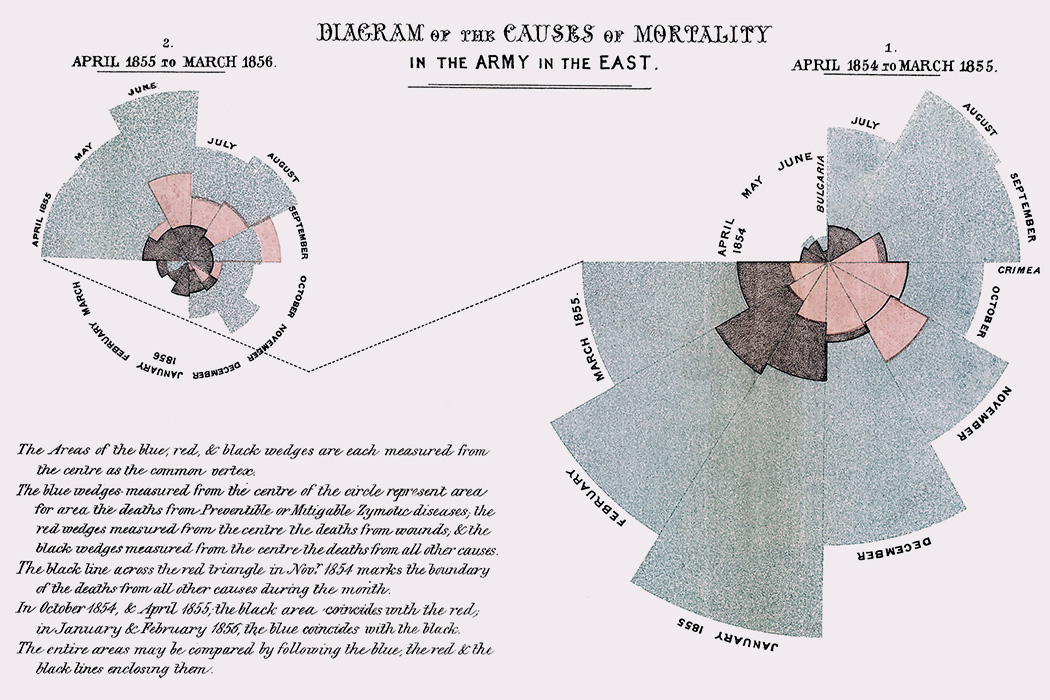
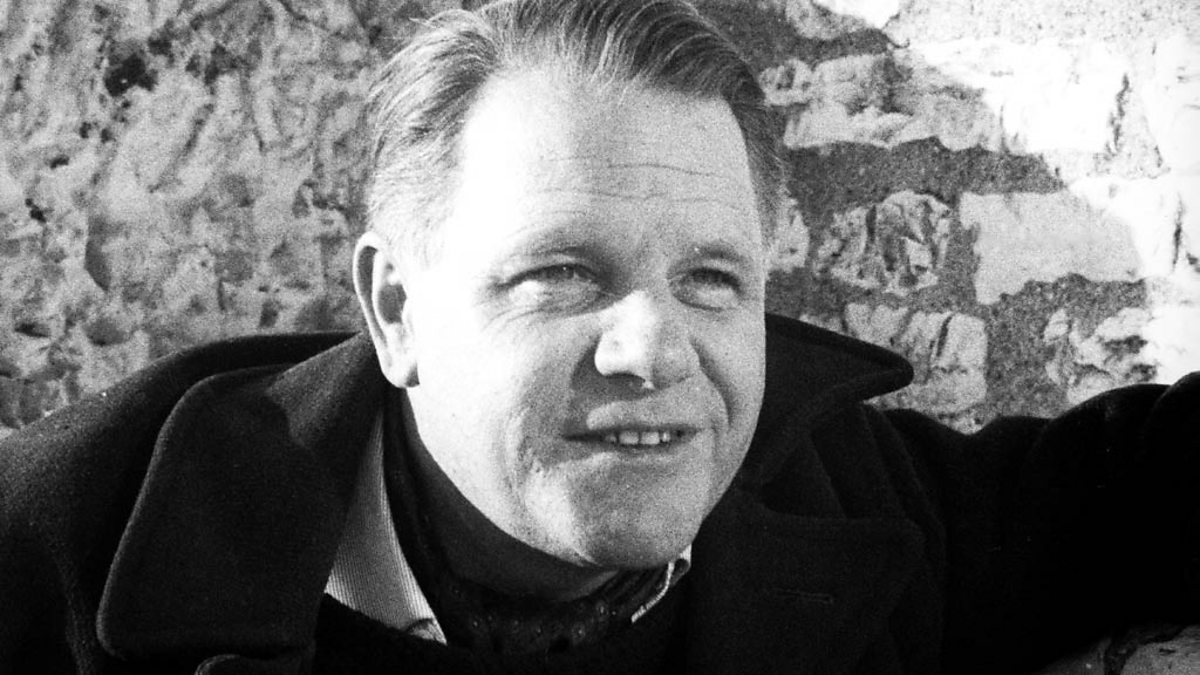

 Neither my companion nor I had read a single word of this almighty author at the time. As I was to learn only in the last few months, I missed the teenage ritual of diving into Durrell by about five to ten years. Justine, Balthazar, Mountolive, and Clea. These were the four volumes read by an impressionable generation just before me. My older literary friends describe soaking up Durrell’s words with wide and voracious eyes around seventeen — just before they joined the less exclusive liturgical practice of tossing their tasseled caps into the heavens preceding the uncertain foray into higher education and the newfound duty of negotiating injurious capitalism (clearly not redeemable by taxation these days, contrary to sentiments expressed by the novelist Pursewarden in Mountolive).
Neither my companion nor I had read a single word of this almighty author at the time. As I was to learn only in the last few months, I missed the teenage ritual of diving into Durrell by about five to ten years. Justine, Balthazar, Mountolive, and Clea. These were the four volumes read by an impressionable generation just before me. My older literary friends describe soaking up Durrell’s words with wide and voracious eyes around seventeen — just before they joined the less exclusive liturgical practice of tossing their tasseled caps into the heavens preceding the uncertain foray into higher education and the newfound duty of negotiating injurious capitalism (clearly not redeemable by taxation these days, contrary to sentiments expressed by the novelist Pursewarden in Mountolive).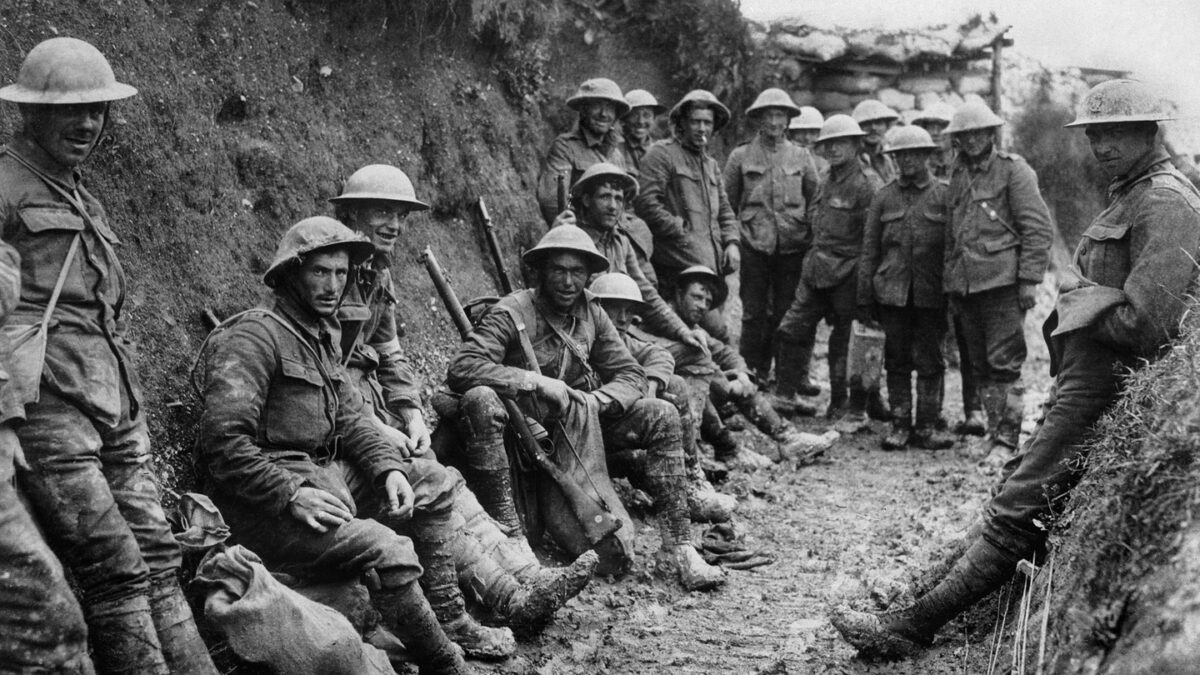
 The men went to war. Their psyches were scarred and sotted by the sights and sounds of death and dreary dissolution — all doled out at a hellish and unprecedented new normal. Machine guns, mustard gas, the ear-piercing shrieks of shrapnel and shells, rats gnawing on nearby corpses. The lush fields of France anfracted into a dark flat wasteland.
The men went to war. Their psyches were scarred and sotted by the sights and sounds of death and dreary dissolution — all doled out at a hellish and unprecedented new normal. Machine guns, mustard gas, the ear-piercing shrieks of shrapnel and shells, rats gnawing on nearby corpses. The lush fields of France anfracted into a dark flat wasteland.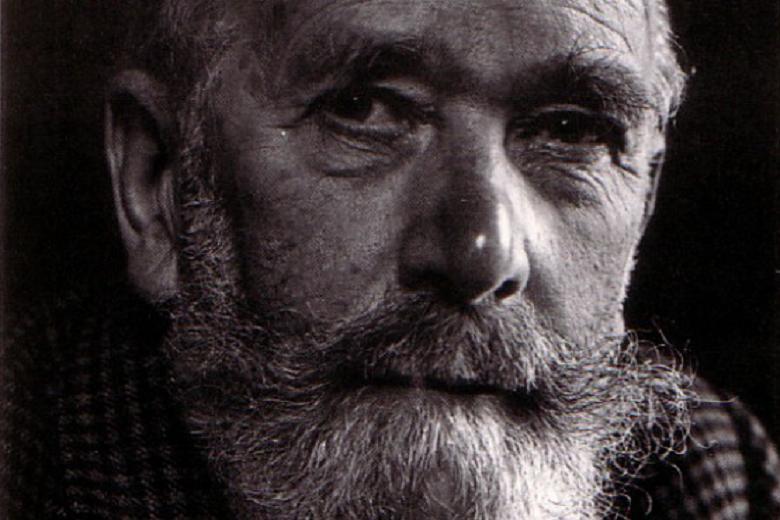 
 Thankfully, I had no such qualms with High Wind; in large part because, unlike Golding, Hughes isn’t so obsessed with plugging in values — the novel as a Sudoku puzzle? — to uphold his Great AllegoryTM (and thus literary posterity). The older you get as a reader, the more you welcome the fresh shock of the visceral: those exotic and sometimes unsettling voices you may not encounter in the real world.
Thankfully, I had no such qualms with High Wind; in large part because, unlike Golding, Hughes isn’t so obsessed with plugging in values — the novel as a Sudoku puzzle? — to uphold his Great AllegoryTM (and thus literary posterity). The older you get as a reader, the more you welcome the fresh shock of the visceral: those exotic and sometimes unsettling voices you may not encounter in the real world. 
 I’ve delivered variations of these sentiments over the phone to amused literary friends, who, when they weren’t laughing their asses off over my five minute anti-Naipaul soliloquies, were good enough to urge me to forgo the semi-scholarly format of this ridiculous years-long project and simply speak from the heart. I shall do my best to be as thoughtful as I can about my Naipaul bellicosity, which is, alas, the only way to move forward with this project. I can tell you this much. Not even
I’ve delivered variations of these sentiments over the phone to amused literary friends, who, when they weren’t laughing their asses off over my five minute anti-Naipaul soliloquies, were good enough to urge me to forgo the semi-scholarly format of this ridiculous years-long project and simply speak from the heart. I shall do my best to be as thoughtful as I can about my Naipaul bellicosity, which is, alas, the only way to move forward with this project. I can tell you this much. Not even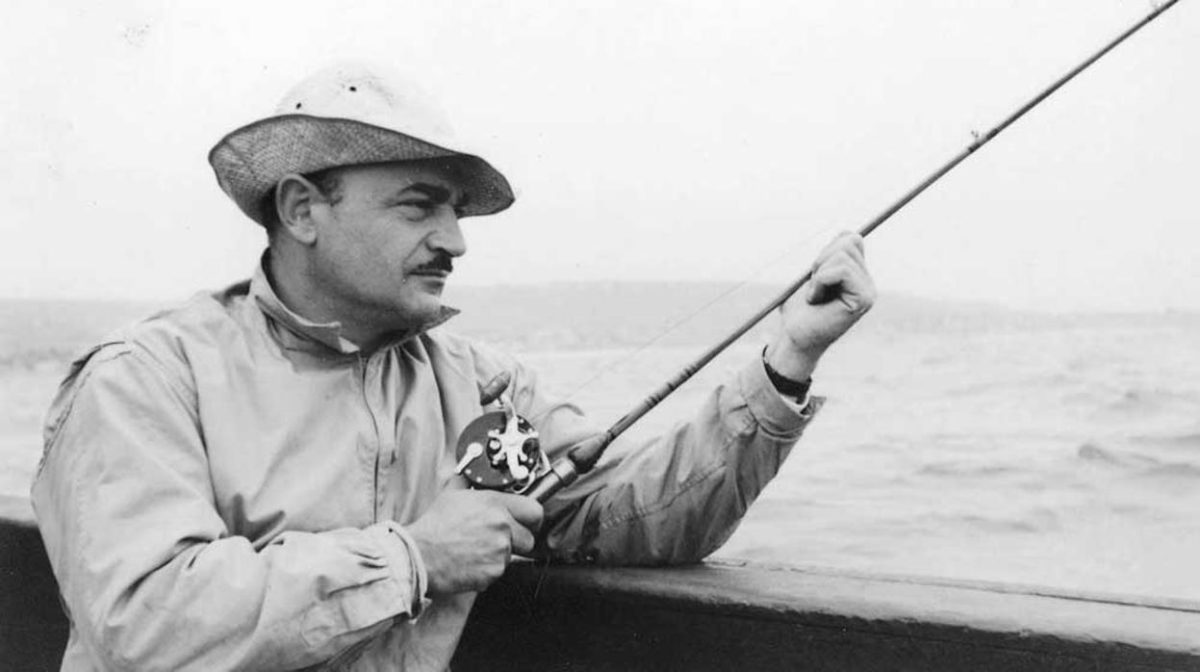 
 Both men had turned to screenwriting to stay afloat during the Great Depression. Both men had much to say about the traps and illusions of American life. But it would take longer for West to be reassessed and appreciated — in large part because he was arguably fiercer than Fitz with his fiction. He had his finger firmly on the troubling pulse of feral American life and he wasn’t afraid to use it with the other nine at his typewriter. In a short essay called “Some Notes on Violence,” West pointed to the idiomatic violence that had permeated every corner of printed media: “We did not start with the ideas of printing tales of violence. We now believe that we would be doing violence by suppressing them.” His razor-sharp satire featured philandering dwarves, skewered the hideous contradictions of gaudy Hollywood spectacle, and, in just one of many enthralling flashes of his grimly hilarious invention, depicted a dead horse serving as au courant decor at the bottom of a swimming pool. (In an age in which urine-drinking is prescribed as a COVID remedy and reality star Stephanie Matto makes $200,000 selling her farts in a jar, one wonders why the present fictional landscape doesn’t reflect our scabrous realities and why 85% of today’s gatekeepers are so hostile to such a necessary dialogue between fiction and life. But then this is the same universe in which Hanya Yanagihara’s excellent, quite readable, and wildly ambitious new novel, To Paradise,
Both men had turned to screenwriting to stay afloat during the Great Depression. Both men had much to say about the traps and illusions of American life. But it would take longer for West to be reassessed and appreciated — in large part because he was arguably fiercer than Fitz with his fiction. He had his finger firmly on the troubling pulse of feral American life and he wasn’t afraid to use it with the other nine at his typewriter. In a short essay called “Some Notes on Violence,” West pointed to the idiomatic violence that had permeated every corner of printed media: “We did not start with the ideas of printing tales of violence. We now believe that we would be doing violence by suppressing them.” His razor-sharp satire featured philandering dwarves, skewered the hideous contradictions of gaudy Hollywood spectacle, and, in just one of many enthralling flashes of his grimly hilarious invention, depicted a dead horse serving as au courant decor at the bottom of a swimming pool. (In an age in which urine-drinking is prescribed as a COVID remedy and reality star Stephanie Matto makes $200,000 selling her farts in a jar, one wonders why the present fictional landscape doesn’t reflect our scabrous realities and why 85% of today’s gatekeepers are so hostile to such a necessary dialogue between fiction and life. But then this is the same universe in which Hanya Yanagihara’s excellent, quite readable, and wildly ambitious new novel, To Paradise, 
 I’ve been a city man all my life. Certainly all of my adult life. At the age of twenty, I escaped from the dour doldrums of suburban Sacramento — the kind of hideous Flintstones-style recurring backdrop that seems to encourage broken dreams, angry tears, and rampant abuse behind model home replica doors — for the bright foggy beauty and the joyful pastels of San Francisco.
I’ve been a city man all my life. Certainly all of my adult life. At the age of twenty, I escaped from the dour doldrums of suburban Sacramento — the kind of hideous Flintstones-style recurring backdrop that seems to encourage broken dreams, angry tears, and rampant abuse behind model home replica doors — for the bright foggy beauty and the joyful pastels of San Francisco. 
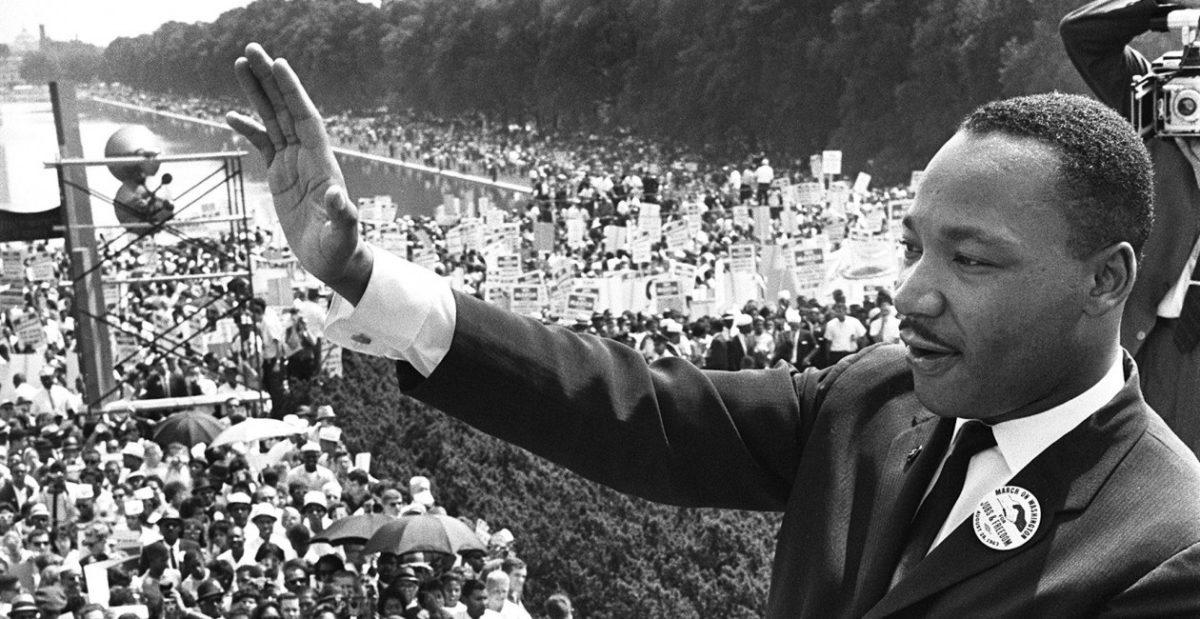


 It was a warm day in April when Dr. Martin Luther King was arrested. It was the thirteenth and the most important arrest of his life. King, wearing denim work pants and a gray fatigue shirt, was manacled along with fifty others that afternoon, joining close to a thousand more who had bravely submitted their bodies over many weeks to make a vital point about racial inequality and the unquestionable inhumanity of segregation.
It was a warm day in April when Dr. Martin Luther King was arrested. It was the thirteenth and the most important arrest of his life. King, wearing denim work pants and a gray fatigue shirt, was manacled along with fifty others that afternoon, joining close to a thousand more who had bravely submitted their bodies over many weeks to make a vital point about racial inequality and the unquestionable inhumanity of segregation.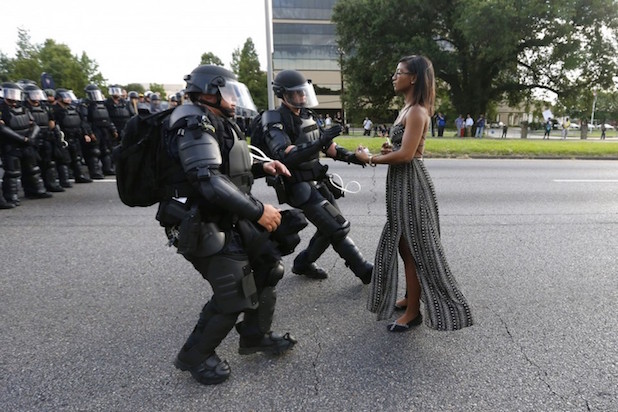 
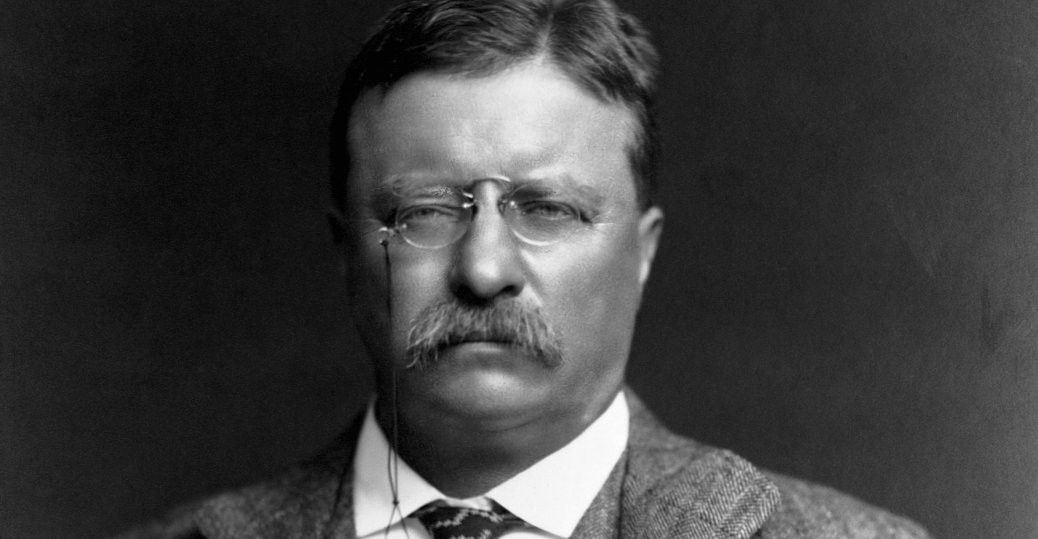

 One of many blistering tangerines contained within Mark Twain’s juicy three volume Autobiography involves his observations on Theodore Roosevelt: “We have never had a President before who was destitute of self-respect and of respect for his high office; we have had no President before who was not a gentleman; we have had no President before who was intended for a butcher, a dive-keeper or a bully, and missed his mission of compulsion of circumstances over which he had no control.”
One of many blistering tangerines contained within Mark Twain’s juicy three volume Autobiography involves his observations on Theodore Roosevelt: “We have never had a President before who was destitute of self-respect and of respect for his high office; we have had no President before who was not a gentleman; we have had no President before who was intended for a butcher, a dive-keeper or a bully, and missed his mission of compulsion of circumstances over which he had no control.” 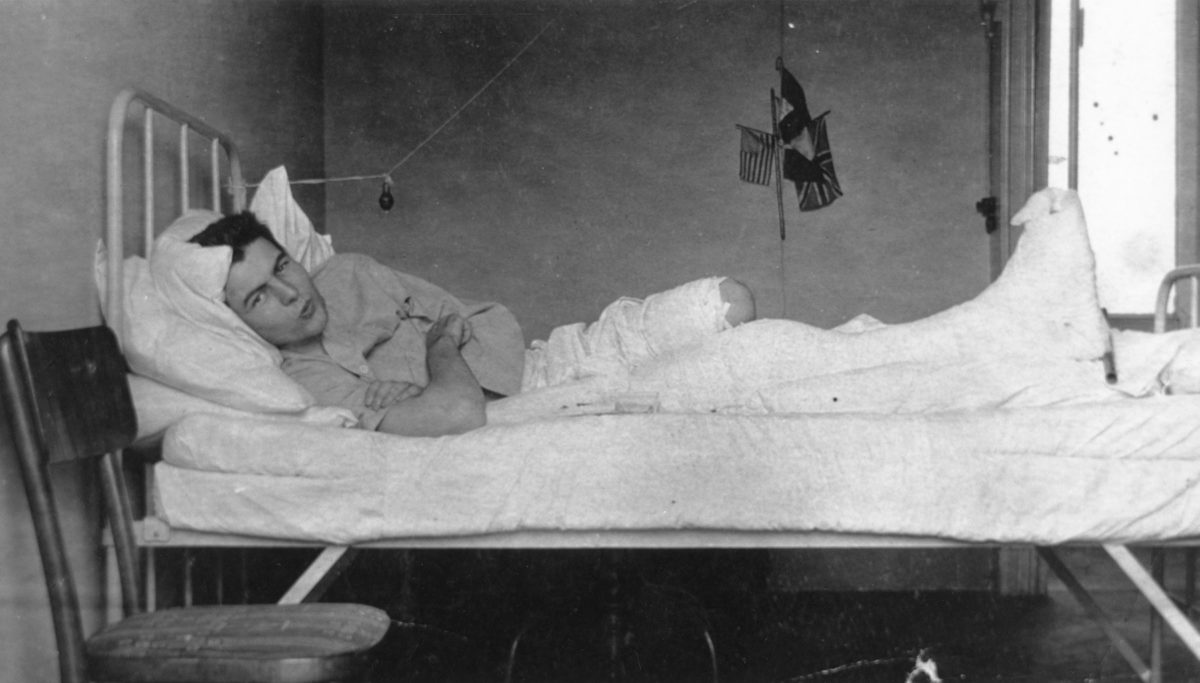
 You likely know the basics: An American goes to Italy and enlists as a “tenente.” He drives a battlefield ambulance just before his nation enters World War I. He gets wounded. He meets a nurse at a hospital. He falls in love. He feels free as he recovers. He feels trapped as he returns to the front. He gets disillusioned. He flees. He finds her again. Bad things happen. But A Farewell to Arms is so much more than this. It is a heartbreaking love story. It is a remarkably subtle indictment of war. It shows how people bury their romantic longings behind duty and how there’s a greater bravery in fulfilling what you owe to your heart. It argues for life and love. Its final paragraph is devastating. It zooms along with masterly prose that is buried with treasure. It is one of the greatest novels of the early 20th century. This statement is not hyperbole.
You likely know the basics: An American goes to Italy and enlists as a “tenente.” He drives a battlefield ambulance just before his nation enters World War I. He gets wounded. He meets a nurse at a hospital. He falls in love. He feels free as he recovers. He feels trapped as he returns to the front. He gets disillusioned. He flees. He finds her again. Bad things happen. But A Farewell to Arms is so much more than this. It is a heartbreaking love story. It is a remarkably subtle indictment of war. It shows how people bury their romantic longings behind duty and how there’s a greater bravery in fulfilling what you owe to your heart. It argues for life and love. Its final paragraph is devastating. It zooms along with masterly prose that is buried with treasure. It is one of the greatest novels of the early 20th century. This statement is not hyperbole.














